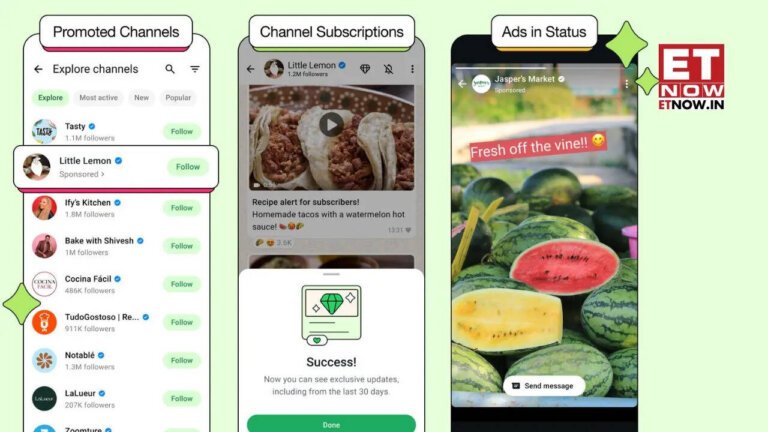
Messaging app WhatsApp has introduced advertisements for the first time, changing its previous ad-free policy. Ads will initially appear only in the Updates tab, specifically in the Status section, and will not interfere with personal messaging. The company emphasized that personal messages, calls, and statuses remain end-to-end encrypted, and it will not sell or share users' phone numbers with advertisers. Ads will be targeted based on user location, language, and previous ad interactions, and users linked to the Accounts Center may see ads influenced by their activity on other Meta platforms. WhatsApp's founders previously expressed their commitment to an ad-free experience in a 2012 blog post, arguing that advertising detracts from the user experience. WhatsApp was not always free; it originally charged an annual subscription fee of [openai_gpt model="gpt-4o-mini" prompt="Summarize the content and extract only the fact described in the text bellow. The summary shall NOT include a title, introduction and conclusion. Text: Messaging app WhatsApp has taken a significant step by introducing advertisements for the first time, marking a notable shift from its original stance against ads. Historically, the app, known for its distinctive bright green interface, prided itself on being ad-free, a rarity among major tech platforms. In a 2012 blog post, WhatsApp co-founders expressed their commitment to a user-focused experience, famously quoting Tyler Durden from Fight Club: “Advertising has us chasing cars and clothes, working jobs we hate so we can buy shit we don’t need.”
However, the recent announcement titled “Helping you Find More Channels and Businesses on WhatsApp” reveals that the app will now feature ads, albeit initially limited to the Updates tab. This means users can expect to see advertisements in the Status section, akin to the 24-hour Stories feature found on other Meta platforms like Instagram and Facebook, without disrupting their private messaging experience.
What’s new? Adverts (Picture: Shutterstock)
WhatsApp reassured users that those who primarily use the app for personal communication will not notice any changes to their messaging experience. This transition aligns WhatsApp more closely with its parent company Meta’s other applications, which are heavily ad-supported.
How will apps be targeted?
Meta has emphasized that the introduction of ads will be handled with privacy in mind. The company stated that personal messages, calls, and statuses will remain end-to-end encrypted, ensuring that no one, including Meta, can access them. Ads will be tailored based on factors such as location, language, and user interactions with previous advertisements. Additionally, users who have linked their WhatsApp accounts to the Accounts Center may receive ads influenced by their activity across other Meta platforms.
How the new ads will look (Picture: Meta)
Meta has committed to never selling or sharing users' phone numbers with advertisers and has assured that personal messages will not be utilized for targeted advertising.
What did WhatsApp say about ads previously?
Reflecting on its past, WhatsApp’s founders articulated their aversion to advertising in a 2012 blog post, stating, “No one wakes up excited to see more advertising.” They emphasized their dedication to enhancing user experience rather than focusing on ad revenue, arguing that the presence of ads detracts from the core mission of providing reliable messaging. They maintained that their engineering efforts were directed towards improving the app rather than mining user data.
The blog post from June 2012 (Picture: WhatsApp)
‘The beginning of deeper data collection’?
Despite assurances from Meta regarding user privacy, some industry experts express concerns that this move could signal a broader shift towards increased data collection. Marijus Briedis, Chief Technology Officer at NordVPN, remarked that the introduction of ads in messaging apps often precedes more invasive data practices. He cautioned that while Meta claims chats remain private, its business model fundamentally relies on data-driven surveillance. Briedis urged European users to remain vigilant, as the gradual introduction of ads could lead to a future where private messaging becomes monetized and monitored.
Changes are coming (Picture: Meta)
Was WhatsApp always free?
WhatsApp was not always a free service; it originally charged an annual subscription fee of [cyberseo_openai model="gpt-4o-mini" prompt="Rewrite a news story for a business publication, in a calm style with creativity and flair based on text below, making sure it reads like human-written text in a natural way. The article shall NOT include a title, introduction and conclusion. The article shall NOT start from a title. Response language English. Generate HTML-formatted content using tag for a sub-heading. You can use only , , , , and HTML tags if necessary. Text:
What’s new? Adverts (Picture: Shutterstock)
Messaging app WhatsApp has introduced adverts for the first time, a departure from the anti-ad ethos it had when first set up.
The famous bright green app had been unusual in major tech apps in not allowing adverts on the platform.
‘We don’t sell ads’, they said in a 2012 blog post quoting Tyler Durden from Fight Club: ‘Advertising has us chasing cars and clothes, working jobs we hate so we can buy shit we don’t need.’
Now, even they will be sending us to chase cars, clothes, doggy sunglasses, and mini washing machines for underwear that fit on your bedside table.
A new post titled, euphemistically, ‘Helping you Find More Channels and Businesses on WhatsApp’, revealed the change yesterday.
For now, ads will only be seen in the Updates tab.
This means you won’t see ads for vitamins or foot scrubs popping up in between your private messages.
How the new ads will look (Picture: Meta)
The company said: ‘If you only use WhatsApp to chat with friends and loved ones there is no change to your experience at all.’
But it marks a shift towards becoming more like Meta’s ad-heavy other big apps, Instagram and Facebook.
For now, ads will only appear in Status, which is similar to the 24-hour Stories function on their other apps.
How will apps be targeted?
Meta said they had built these features ‘in the most private way possible’: ‘Your personal messages, calls, and statuses remain end-to-end encrypted, meaning no one (not even us) can see or hear them.’
They said they would use information like country or city, language, Channels followed, and previous ad interaction to guide which ads are shown.
Changes are coming (Picture: Meta)
Those who had added WhatsApp to Accounts Center could be shown ads based on information from across their other Meta accounts too.
They promised they would ‘never sell or share your phone number to advertisers’ and personal messages and calls would not be used for targeted ads.
What did WhatsApp say about ads previously?
A 2012 blog post from founders Jan Koum and Brian Acton said: ‘No one wakes up excited to see more advertising, no one goes to sleep thinking about the ads they’ll see tomorrow.
‘We know people go to sleep excited about who they chatted with that day (and disappointed about who they didn’t). We want WhatsApp to be the product that keeps you awake… and that you reach for in the morning. No one jumps up from a nap and runs to see an advertisement.
The blog post from June 2012 (Picture: WhatsApp)
‘Advertising isn’t just the disruption of aesthetics, the insults to your intelligence and the interruption of your train of thought.
‘At every company that sells ads, a significant portion of their engineering team spends their day tuning data mining, writing better code to collect all your personal data, upgrading the servers that hold all the data and making sure it’s all being logged and collated and sliced and packaged and shipped out… And at the end of the day the result of it all is a slightly different advertising banner in your browser or on your mobile screen.
‘Remember, when advertising is involved you the user are the product.
‘At WhatsApp, our engineers spend all their time fixing bugs, adding new features and ironing out all the little intricacies in our task of bringing rich, affordable, reliable messaging to every phone in the world. That’s our product and that’s our passion. Your data isn’t even in the picture. We are simply not interested in any of it.
‘When people ask us why we charge for WhatsApp, we say “Have you considered the alternative?’
‘The beginning of deeper data collection’?
Meta has insisted that personal messages will be unchanged, but some fear this move could be opening the door to more significant changes later.
Marijus Briedis, Chief Technology Officer at NordVPN, said: ‘Ads in WhatsApp aren’t just a distraction – they’re a signal of what may come next.
‘When advertising enters a messaging app, it often marks the beginning of deeper data collection. Meta says your chats are private, but its business model relies on data-driven surveillance. This isn’t just about pop-ups; it’s about protecting your privacy.
Ads will be kept away from personal messages – at least for now (Picture: Meta)
‘Europe’s data protection laws were created to guard against exactly this kind of gradual overreach. Meta’s so-called ‘optional’ data-sharing is rarely as optional as it sounds – there’s often a trade-off, and too often, that trade-off is your personal information.
‘We’ve seen this pattern before, with small updates that pave the way for much bigger changes. The introduction of ads could signal a wider shift away from private messaging toward monetised, monitored communication. European users should pay close attention – your messages may not stay as private as you think.’
Was WhatsApp always free?
No. In its early years, there was an annual subscription fee of $0.99 (which worked out at around 64p to 69p in the UK).
Imposed after the first year (which was free), this was part the reason they could afford to go without ads.
When Facebook bought the company in 2016, they scrapped the charge to focus on growth, saying some users were worried about losing access if they didn’t have a debit or credit card number.
They still didn’t introduce ads at the time, saying they wanted to explore other ways of making money from WhatsApp, like making the app a tool to communicate information with businesses and organisations such as banks and airlines.
Get in touch with our news team by emailing us at webnews@metro.co.uk.
For more stories like this, check our news page.
MORE: Eminem’s music company ‘sues Meta for $109,000,000 over 243 of his songs’
MORE: Family business ‘£10,000 out of pocket’ after Meta blocks their accounts for 12 weeks
News Updates
Stay on top of the headlines with daily email updates." temperature="0.3"].99 after the first year of use. This model allowed the app to operate without advertisements. Following Facebook's acquisition of WhatsApp in 2016, the subscription fee was eliminated to promote user growth, with the company exploring alternative revenue streams, such as facilitating communication for businesses and organizations. " max_tokens="3500" temperature="0.7" top_p="1.0" best_of="1" presence_penalty="0.1" frequency_penalty="frequency_penalty"].99 before Facebook acquired the company in 2016 and eliminated the fee to encourage growth.