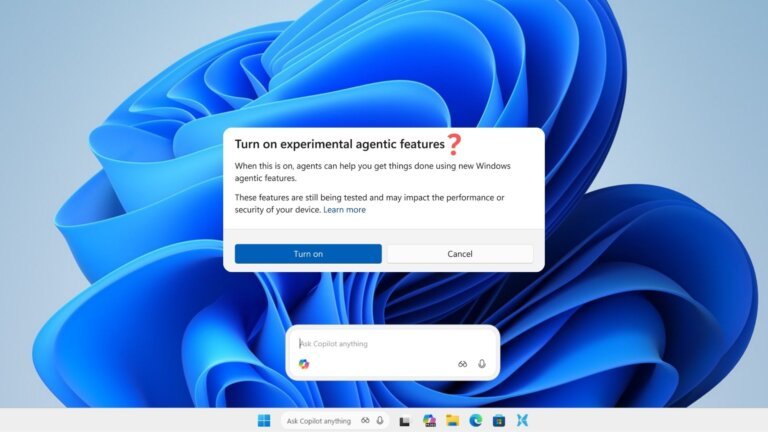
Microsoft is transitioning its Windows operating system to an "AI-native" platform, embedding AI capabilities directly into the Windows kernel, marking a significant architectural shift not seen in three decades. This new approach, called the "Agentic OS," allows AI to manage files, system settings, and workflows proactively. The updated kernel, partially rewritten in Rust, includes a new NPU-aware scheduler that treats the Neural Processing Unit as a primary resource. Microsoft has introduced "Agent Workspace" and "Agent Accounts" for autonomous agents, ensuring actions are logged and audited for compliance. Communication between agents and the system is facilitated by the Model Context Protocol (MCP). Hardware requirements for the new OS have increased, with benchmarks set for NPUs achieving 80 to 100 TOPS. Major PC manufacturers are adjusting their portfolios to accommodate "Agentic PCs." The competitive landscape is evolving, with companies like Alphabet and Apple developing their own AI-native platforms. The introduction of the AI-native kernel raises privacy and security concerns, with Microsoft implementing measures to restrict third-party access to the kernel. Future updates may include "self-healing" capabilities and "Cross-Device Agency," leading to a more integrated personal AI experience.