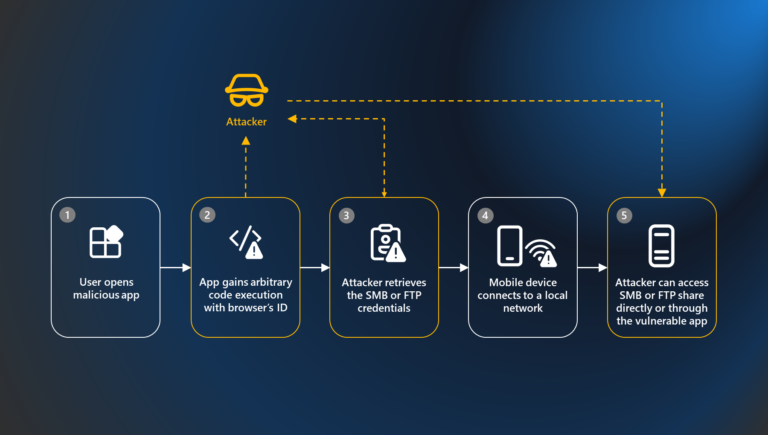
A new class of Android attacks called Pixnapping allows installed applications to monitor the content displayed by other apps without requesting permissions. This attack can capture sensitive information, including Gmail previews, Google Maps timelines, and two-factor authentication codes, by exploiting Android’s rendering APIs and a hardware side channel. Pixnapping operates by manipulating Android intents to funnel pixels from a target app into the system's rendering pipeline, using timing variations from GPU compression to recover text. The attack has been demonstrated on various devices, including Google Pixel models 6 through 9 and the Samsung Galaxy S25. In February 2025, the vulnerability was disclosed to Google, which assigned it a CVE-2025-48561 rating and classified it as high risk. A patch was released in September, but a workaround was found, leading to ongoing collaboration with Google and Samsung for further fixes. Users are advised to maintain good app hygiene, avoid unknown APKs, and promptly install security updates. The researchers have not yet developed a universal mitigation app and advocate for platform-level fixes to address the vulnerabilities.