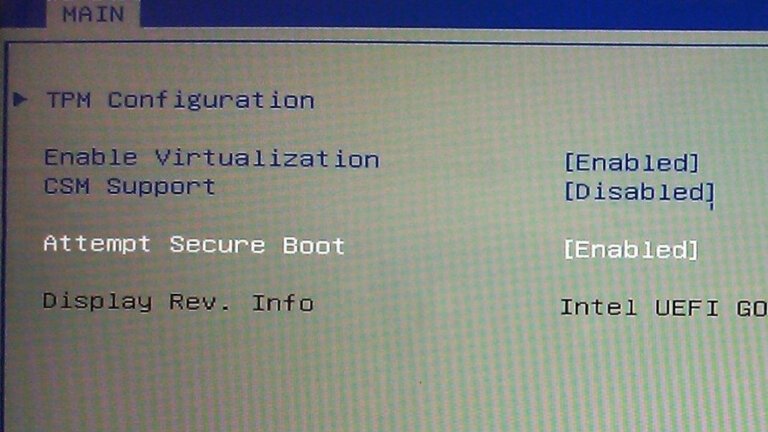
Microsoft will begin rolling out new Secure Boot certificates through Windows Update starting in March 2026, coinciding with the expiration of original certificates from 2011, which will phase out in June 2026. The new certificates include Microsoft Corporation KEK 2K CA 2023, Microsoft UEFI CA 2023, Microsoft Option ROM UEFI CA 2023, and Windows UEFI CA 2023. Not all Windows users will receive the update simultaneously; eligibility will focus on high-confidence devices with strong update histories. Newer PCs sold from 2024 will already have the 2023 Secure Boot certificates, while some devices may require additional firmware updates from their OEMs. PCs that do not receive the new certificates will still boot but will operate with diminished security, increasing vulnerability to exploits and compatibility issues with anti-cheat software and future Windows versions. Users on unsupported Windows versions will not receive the new certificates, leading to heightened security risks after June 2026.