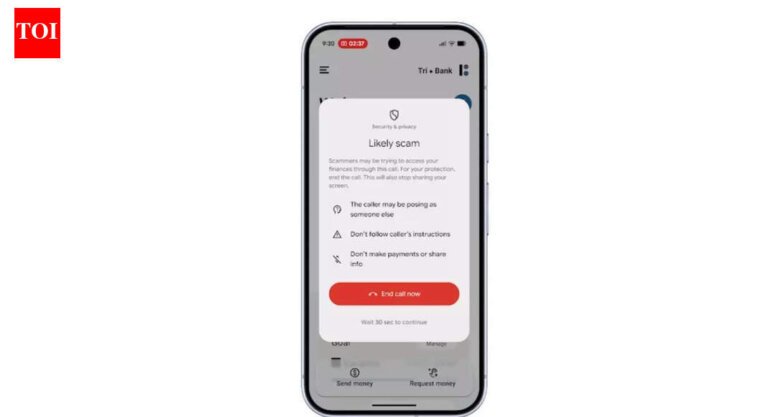
When connecting to public Wi-Fi, using a VPN is essential as it encrypts traffic and creates a secure tunnel between the device and a remote server, keeping activities concealed from the local network. Android devices continuously communicate in the background, performing tasks such as updating emails and syncing notes, which increases data visibility on public networks. Public Wi-Fi has become common due to remote work and shared spaces, leading to increased privacy risks as smartphones now store sensitive information like banking apps and personal photos. Users are encouraged to adopt simple security habits, including using a VPN when connecting to public networks. Android devices are always connected, making network-level protection important to safeguard background communications.