Microsoft has released enhancements to Windows 11 in build 26300.7877, including:
- Modern content menu improvements, showing application icons for specific file types when right-clicked.
- Updates to File Explorer with dark mode improvements for the Folder Options dialog.
- Changes to the Settings app for better clarity and usability.
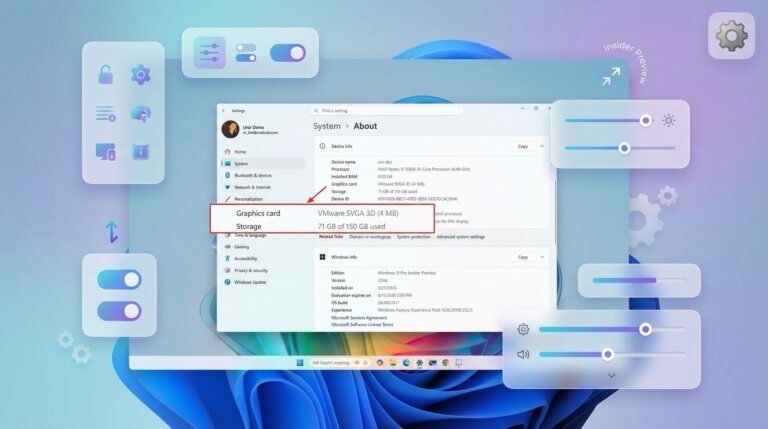
- A redesigned "About" settings page focusing on key hardware specifications.
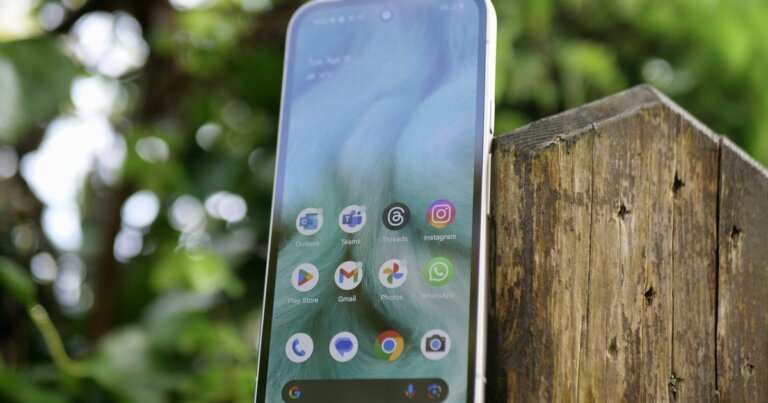
- Introduction of the Cross-Device Resume feature, allowing users to resume applications from Android devices on Windows 11.
- New customization options for the Narrator tool, enabling users to select which properties are read aloud.
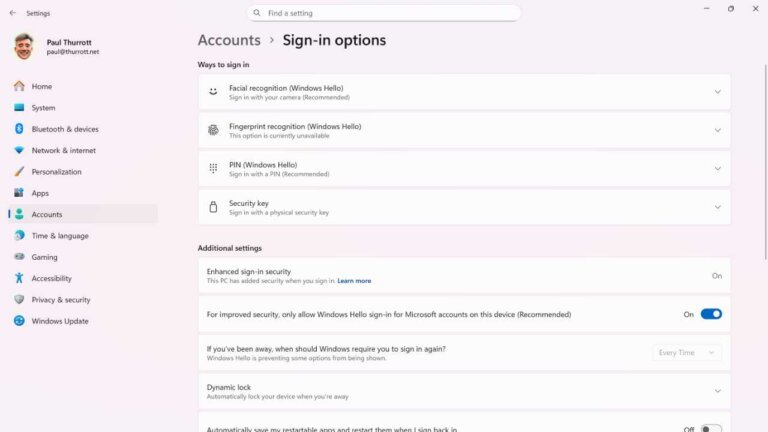
- Windows Hello now supports external biometric fingerprint readers for enhanced security.
- Voice Typing updates allowing users to set a wait time before executing voice commands.
- Redesigned SCOOBE page for a streamlined setup process.
- Expansion of the AI agent in the Settings app to support additional languages.
- Quick Machine Recovery feature enabled by default on Windows 11 Pro editions.
- Camera support for pan and tilt settings accessible from device properties.
- A new network speed test feature available from the Taskbar.
- Improvements to the Widgets dashboard with a new settings page.
Additionally, changes from build 28020.1619 are related to version 26H1, designed for new ARM64 hardware expected in 2026, and the Canary Channel has been divided into two paths for different versions.