Microsoft has discontinued the Windows Subsystem for Android and its integration with the Amazon Appstore on Windows 11 due to low demand. Users can no longer use an official Microsoft method to install general Android apps. The primary alternatives are Google Play Games on PC, which focuses on gaming, and third-party emulators like BlueStacks, LDPlayer, and GameLoop for a broader range of applications.
To use Google Play Games, users need a PC with at least 8 GB RAM, a modern quad-core processor, hardware-accelerated graphics, SSD storage with 10 GB free, and hardware virtualization enabled. Users must enable virtualization in their UEFI or BIOS settings and activate the Virtual Machine Platform and Windows Hypervisor Platform in Windows.
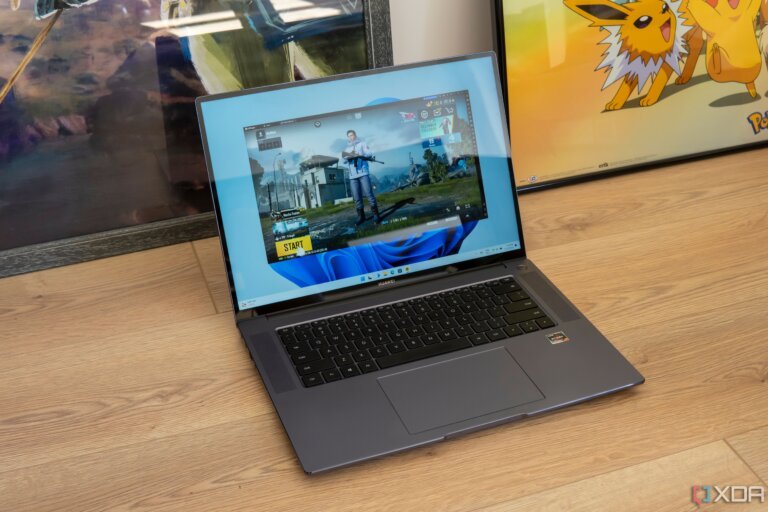
Emulators allow users to run full Android apps on Windows. They can download apps from the Google Play Store within the emulator or sideload APK files. Users should be cautious about security risks when sideloading apps and stick to reputable sources.
Performance tuning for emulators involves allocating sufficient resources, resolving virtualization conflicts, and optimizing settings like resolution and frame rate. Users are advised to install on SSDs and minimize background tasks for better performance.