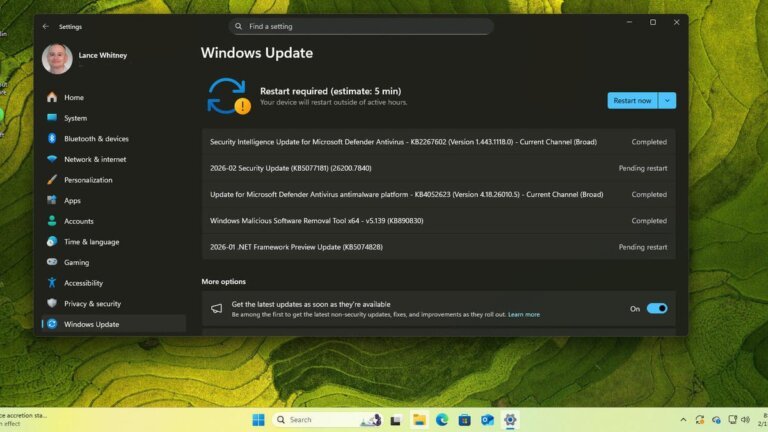
Microsoft's February Patch Tuesday update addresses feature and security bugs, continuing the refresh of Secure Boot certificates to protect against bootkit malware. Secure Boot prevents malicious software from executing during startup by using trusted certificates, many of which are set to expire in June. The update is available for both Windows 11 and Windows 10 users, with the latter needing to be enrolled in the Extended Security Updates (ESU) program until October 2026.
Windows 11 fixes include resolutions for full-screen gaming and WPA3-Personal Wi-Fi connectivity issues, while Windows 10 improvements address Chinese fonts, specific graphics processing units, and custom folder names in File Explorer. A bug causing unexpected restarts in Secure Launch-compatible PCs has also been fixed.
The update includes 55 security patches, a decrease from January's 114, with two classified as critical and six identified as zero-day vulnerabilities. One vulnerability exploited in the wild could allow system privilege escalation, another could disrupt network connectivity, and a third could disable security controls and access sensitive data.
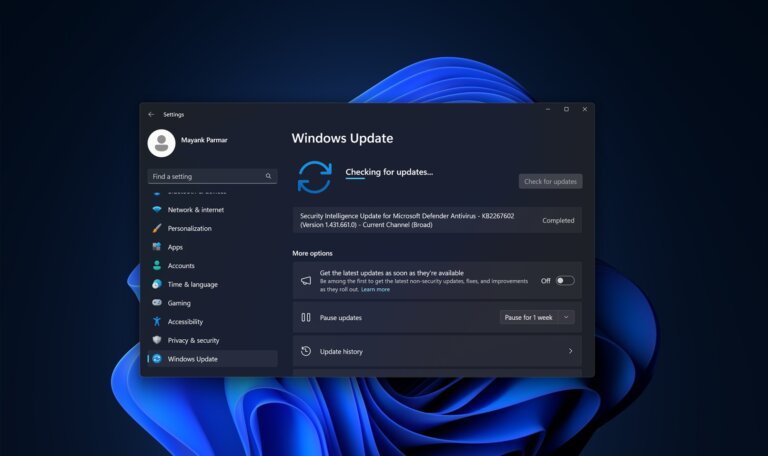
Users can update their Windows 11 PCs through System > Windows Update, and Windows 10 users through System > Update & Security. Due to previous buggy updates, users may consider waiting a few days before installing the February update, with the option to uninstall if issues arise.