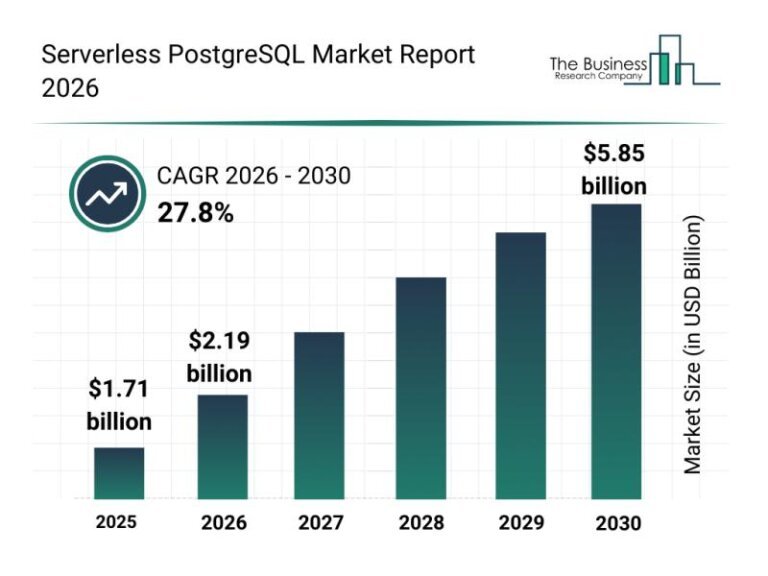
The serverless PostgreSQL market is projected to reach an estimated value of .85 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 27.8%. Key factors driving this growth include the adoption of microservices architectures, deeper integration with cloud ecosystems, the need for rapid deployment, and the rise of SMEs and startups using cloud infrastructure. Notable trends include advancements in serverless orchestration, automation, AI-driven optimization, and innovations in hybrid and multi-cloud solutions. Major players in the market include Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Databricks, among others. A significant event occurred in May 2025 when Databricks acquired Neon Technology to enhance its serverless PostgreSQL offerings. The market is segmented by component, deployment type, organization size, application, and end-user industry, with specific solutions and services outlined for each category.