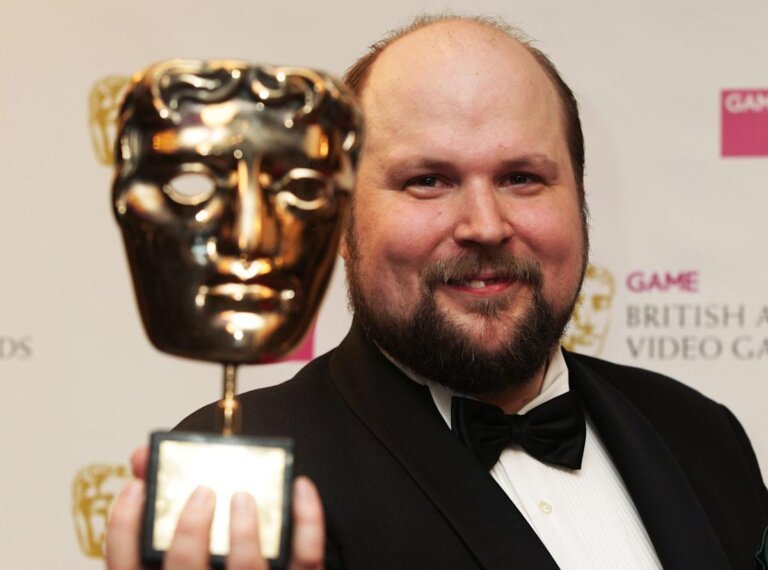
Markus Persson, the creator of Minecraft, has expressed concerns about the rapid integration of generative AI in programming, describing it as an initiative being "forced down our throats" by "evil" entities. He fears losing creative autonomy and control over coding, comparing AI writing code to AI drafting laws. Persson advises aspiring developers to "Learn. Your. Craft," emphasizing the importance of foundational skills in programming. His views align with some industry leaders who advocate for coding literacy as a fundamental skill, while others, like GitHub CEO Thomas Dohmke and Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang, stress the necessity of mastering AI to remain competitive in the job market.