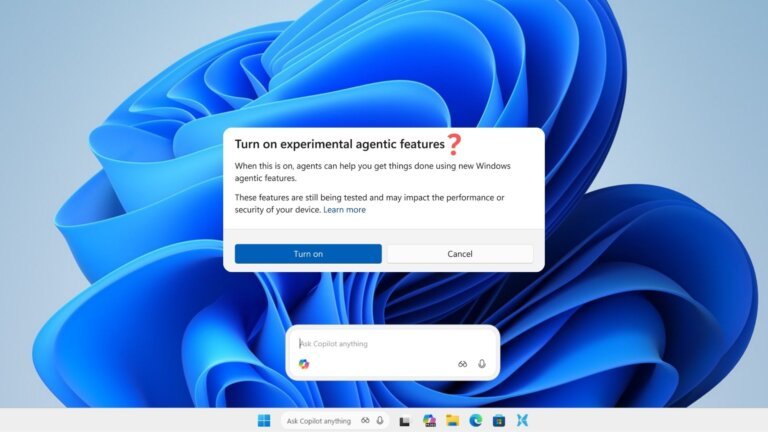
Microsoft has introduced agentic AI capabilities for Windows 11 through the 26220.7262 update, aligning with the trend of using large language models to enhance user experiences. The company has warned about potential risks associated with these new features, including the possibility of "hallucinations" and "novel security risks," specifically highlighting a vulnerability known as cross-prompt injection (XPIA). This flaw could allow malicious content to override agent instructions, leading to unintended actions like data exfiltration or malware installation. Microsoft’s move to integrate these AI features reflects a response to competitive pressures in the tech industry, despite the known flaws and security vulnerabilities associated with them.