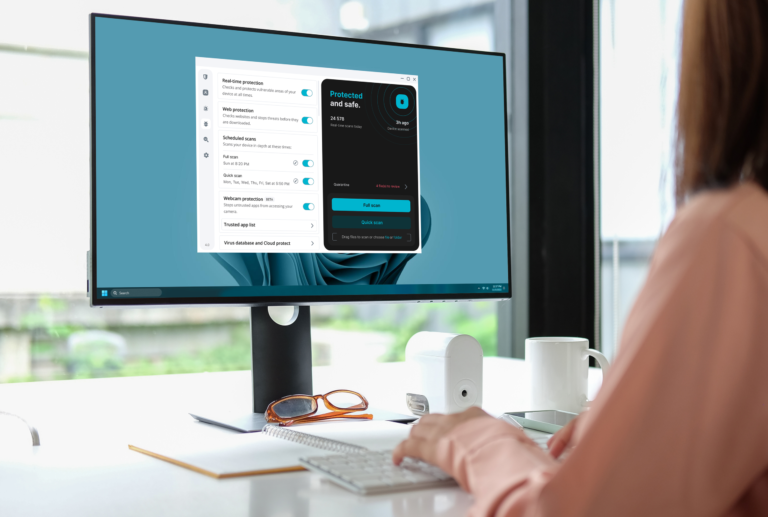
Snowflake Postgres is now generally available on AWS and Azure in all major regions, enabling users to initiate a database in minutes. It integrates transactional and analytical data, accelerating innovation by eliminating complex data pipelines, thus saving time and minimizing risks. Comprehensive resources, including technical documentation, a getting started guide, and a demo overview video, are available for users.