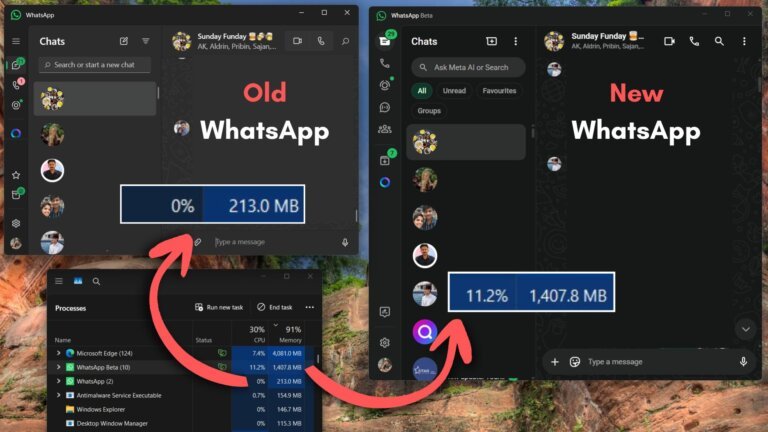
WhatsApp's transition to a Chromium-based web wrapper has resulted in a significant increase in resource consumption for Windows 11 users, with RAM usage reportedly surging to 2GB, compared to less than 1GB for the older version. Users can revert to the older version, which utilizes native code and is more efficient, by following a series of steps involving enabling Developer Mode, downloading a specific package, and using PowerShell commands. The older version maintains a steady resource usage, with memory consumption peaking at 400 MB during status updates and remaining under 300 MB for general messaging. However, reverting to the older version will prevent users from receiving new updates, and it may eventually be phased out by Meta.