Children are increasingly using messaging applications like Messenger for communication, leading to parental concerns over disappearing messages. Parents may want to retrieve deleted messages for reasons such as accidental deletion, bullying, or inappropriate conversations. Deleted Messenger messages may not be permanently erased immediately, and recovery is possible under certain conditions.
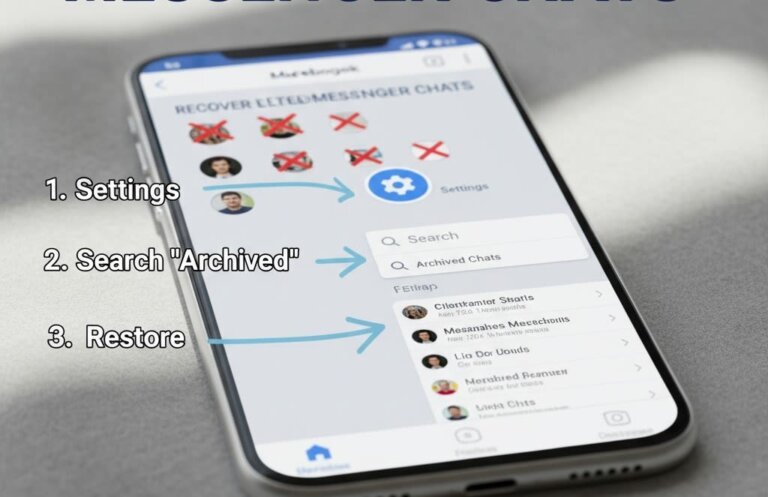
Methods for recovering deleted messages include checking archived conversations, downloading Messenger account data, checking linked devices, and using Messenger tracking apps for parental monitoring. Parents should engage in open communication with their children about safety and establish digital guidelines to foster trust.
To prevent message loss in the future, parents can educate children about archiving versus deleting messages, encourage responsible message management, and promote openness regarding online interactions.