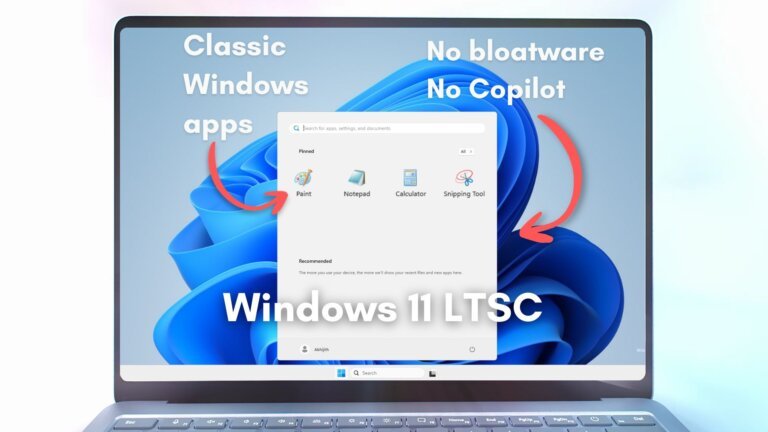
Windows 11 LTSC (Long-Term Servicing Channel) is a specialized edition of Windows 11 designed for organizations that prioritize stability over the latest features. It allows users to defer feature updates for up to ten years, receiving only monthly quality updates and optional feature updates every three years. LTSC includes only Microsoft Edge as a modern app, with classic versions of Calculator, Notepad, and Paint, and lacks Copilot integration, the Microsoft Store, and Widgets. Users can operate LTSC without signing into a Microsoft account. The version was officially announced in April 2023, with Enterprise and IoT editions set to launch in late 2024. It is suitable for large organizations, industrial systems, IT departments, and IoT devices needing long-term support. General users can download a 90-day trial of LTSC, but a clean installation is required for transitioning from Windows 11 Pro or Home. The minimum system requirements include a 1 GHz processor, 4 GB RAM, and 64 GB storage. LTSC offers advantages such as no bloatware, a stable environment, and a lower storage footprint, but it does not receive new Windows features and lacks access to the Microsoft Store by default.