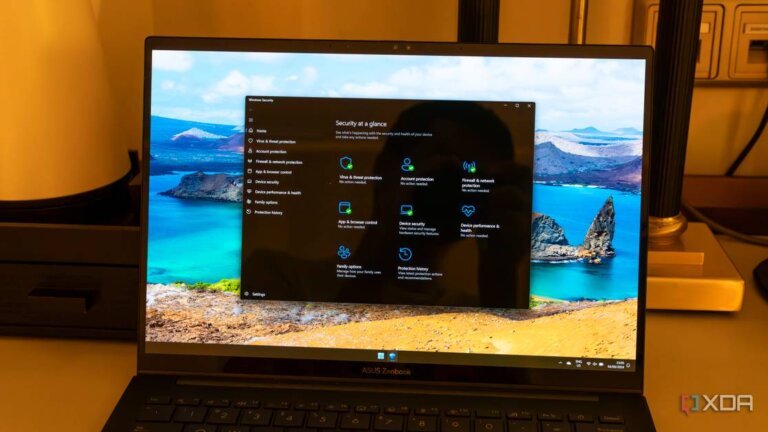
Microsoft's Windows Defender has vulnerabilities that can be exploited by cybercriminals, including a method to remotely disable it using a trusted Windows driver. There has been an increase in counterfeit "Windows Defender" pop-ups that prompt users to call a phone number, connecting them to scammers. These pop-ups do not originate from Microsoft and are often triggered by compromised websites or malicious ads. Scammers use these alerts to gain remote access to victims' computers under the pretense of fixing non-existent issues, often charging for fraudulent services or installing malware. Windows Defender struggles against advanced threats, lacks deeper monitoring capabilities, and is a prime target for attackers due to its widespread use. A multi-faceted security approach, including third-party solutions like Trend Micro, is recommended to address these gaps and enhance protection. Additionally, maintaining smart security habits, such as updating software and using strong passwords, is crucial for overall system security.