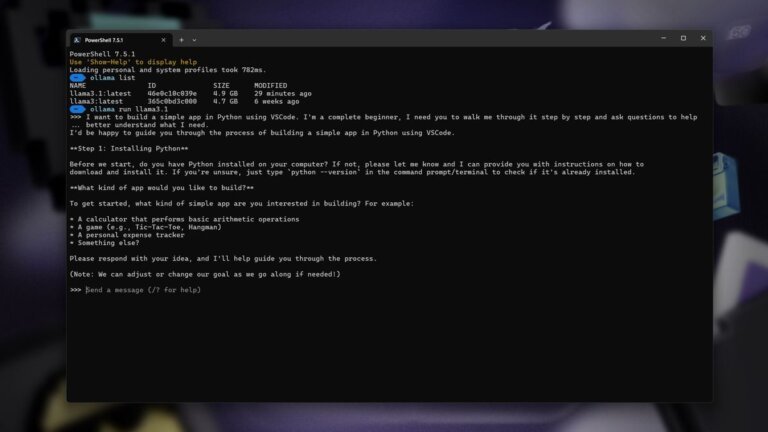
The adoption of AI-powered personal computers is expected to increase significantly in the coming year, driven by Qualcomm's announcement of new AI chips for affordable models priced around 0. Despite the slower evolution of AI software compared to hardware, the relevance of AI in computing is growing, with many applications utilizing AI hardware or neural processing units (NPUs). Microsoft has introduced Copilot+ PCs to promote generative AI tools and encourage the acquisition of Windows 11-compatible hardware. Major chip manufacturers like Intel, Qualcomm, and AMD are developing processors with AI capabilities for these PCs, indicating a shift in the computing landscape.