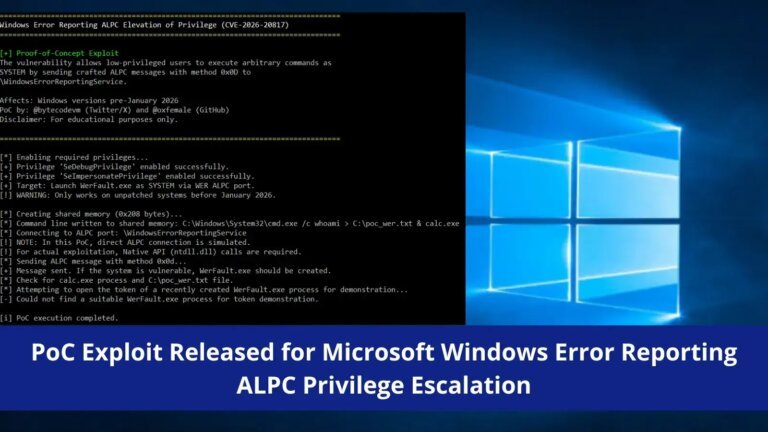
A proof-of-concept exploit for CVE-2026-20817, a local privilege escalation vulnerability in the Windows Error Reporting (WER) service, has been released by security researcher oxfemale on GitHub. This vulnerability allows low-privileged users to gain SYSTEM-level access through crafted Advanced Local Procedure Call (ALPC) messages. The flaw is located in the WER service's SvcElevatedLaunch method, which fails to validate caller privileges before executing WerFault.exe with user-supplied command line parameters. The CVSS v3.1 base score for this vulnerability is 7.8, indicating a high severity level. It affects unpatched versions of Windows 10, Windows 11, Windows Server 2019, and Windows Server 2022 prior to the January 2026 update. Demonstrations have shown successful exploitation on Windows 11 23H2. Security teams are advised to monitor for unusual processes related to WerFault.exe, investigate missing SeTcbPrivilege in SYSTEM tokens, and review WER-related activities from low-privilege users. Immediate application of the January 2026 security patches is recommended, and a temporary workaround involves disabling the WER service.