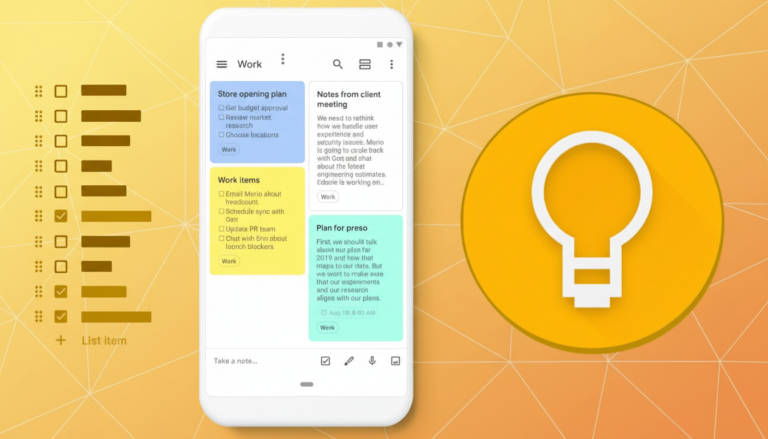
MyRadar has over ten million installations and offers a full-screen radar display, customizable map appearances, and different weather views. A premium subscription is available for [openai_gpt model="gpt-4o-mini" prompt="Summarize the content and extract only the fact described in the text bellow. The summary shall NOT include a title, introduction and conclusion. Text: MyRadar has emerged as a standout in the realm of weather applications, boasting over ten million installations. This app serves not only as a reliable standalone weather tool but also as an excellent secondary resource for radar checks. Users are greeted with a full-screen radar display that is visually appealing on any smartphone. The app allows for customization of the map’s appearance, offering options such as a cool gray default, an aerial view, or a topographic map. Furthermore, users can tailor their weather experience by selecting different views, including satellite imagery or temperature maps. For those seeking more advanced features, a premium subscription is available for .99 a month, providing access to additional weather station data.
MyRadar caters to a diverse audience with its dual offerings. The free version includes in-app purchases to eliminate ads and unlock new radar layers, many of which cater to niche users like pilots. Alternatively, the Pro version comes ad-free, allowing users to explore the app without interruptions. This flexibility in options ensures that users can choose how they wish to engage with the app, aligning with their personal preferences and budget.
Snapseed
In the competitive smartphone market, the quality of a phone's camera remains a pivotal selling point. However, not all devices come equipped with the capability to produce stunning images. Enter Snapseed, a powerful photo editing app that has garnered over one hundred million installations on the Play Store. Its comprehensive feature set makes it an essential tool for anyone serious about photography, regardless of their device.
Snapseed addresses the common imperfections found in mobile photography, offering tools for straightening images, adjusting perspectives, and fine-tuning white balance, colors, and contrast. Its user-friendly interface ensures that these features are easily accessible on smartphones, tablets, and even Chromebooks. For those who find themselves away from their desktop editing software, Snapseed stands out as a top-tier alternative, providing capabilities that surpass many Instagram-centric editors.
Epic Games
While it may raise eyebrows among PC gamers, Epic Games is a must-have for any gamer looking to enhance their Android experience. This video game store and launcher offers a unique proposition: free mobile games every week. Titles such as Machinarium, Subnautica, and Monument Valley II have been part of its generous offerings, aimed at building a loyal user base for its store.
To take advantage of these free games, users simply need to check in every Thursday at 11 AM Eastern to see what’s available. Currently, Epic Games is not listed on the Play Store, requiring users to sideload the APK from the official Epic website. While sideloading carries certain risks, ensuring the APK is sourced directly from Epic mitigates potential security concerns.
KOReader
In an age where smartphones are often used for reading, KOReader stands out as a premier e-reading app, particularly for those who appreciate the nuances of formatting. Originally developed for Kindle and Kobo devices, KOReader has evolved into a favorite among e-book enthusiasts. Its extensive features allow users to customize their reading experience significantly, including altering CSS styles and DPI settings on a per-book basis.
While users will need to provide their own e-books, such as ePubs and PDFs, KOReader's robust functionality makes it an invaluable tool for managing and enjoying a personal library on Android devices. For those who prefer to curate their reading material, KOReader offers an unparalleled experience.
DroidCam
For many Android users, spare devices often collect dust in drawers. However, with DroidCam, those old phones can be transformed into functional webcams. This app supports OBS output, making it an excellent choice for streaming or video conferencing. Whether it’s for a quick Microsoft Teams meeting or a casual Discord chat, repurposing a spare Android phone can save users from investing in a new webcam.
DroidCam is available for free, with optional upgrades for watermark removal and enhanced recording settings at a yearly fee of .99 or a one-time payment of .99. With over one million installations, it has proven itself as a reliable camera app. Although setting up OBS support requires an additional plugin, the effort is worthwhile for those looking to leverage their phone’s camera capabilities for streaming or recording purposes." max_tokens="3500" temperature="0.3" top_p="1.0" best_of="1" presence_penalty="0.1" frequency_penalty="frequency_penalty"].99 a month for advanced features. The app has a free version with in-app purchases to remove ads and unlock new radar layers, while the Pro version is ad-free.
Snapseed has over one hundred million installations and provides tools for editing mobile photos, including straightening images and adjusting colors. It is user-friendly and serves as a powerful alternative to desktop editing software.
Epic Games offers free mobile games weekly, including titles like Machinarium and Subnautica. Users must check in every Thursday at 11 AM Eastern to access these games, and the app requires sideloading from the official Epic website.
KOReader is an e-reading app that allows extensive customization of the reading experience, including altering CSS styles and DPI settings. Users need to provide their own e-books, such as ePubs and PDFs.
DroidCam can transform old Android devices into functional webcams, supporting OBS output for streaming or video conferencing. It is available for free, with optional upgrades for watermark removal and enhanced recording settings. The app has over one million installations.