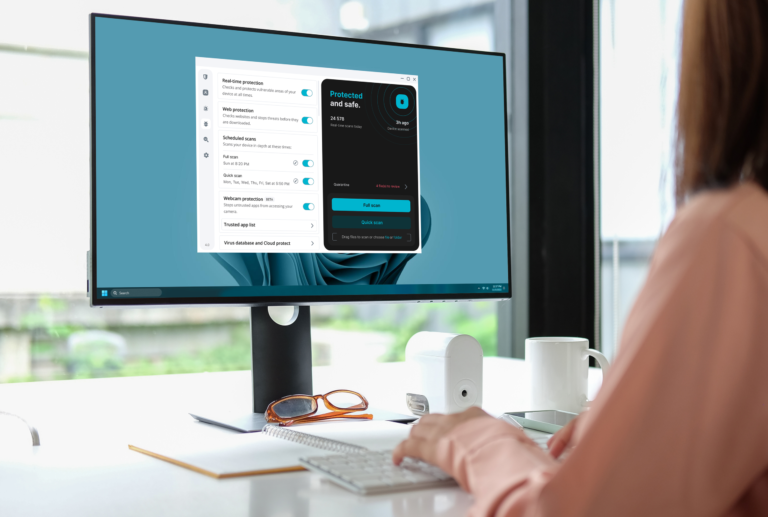
Users are increasingly focused on the effectiveness of their security software alongside the number of streaming services they use. Leading VPN providers are responding by offering comprehensive packages that combine VPN capabilities with antivirus features. Surfshark has introduced Surfshark One, which integrates its VPN service with proprietary antivirus software. This solution is designed to provide a comprehensive cybersecurity experience within a single application.
To access the antivirus feature, users must subscribe to the Surfshark One plan, which offers quick and full scans, customizable scanning options, and scheduled scans. Detected threats are quarantined and deleted after 60 days. The antivirus includes Cloud Protect for continuous defense against malware, updating its database every three hours, and provides 24/7 malware protection.
Surfshark One also includes additional tools such as Alternative ID for safeguarding user information, Surfshark Alert for notifications about compromised sensitive information, and Surfshark Search for ad-free browsing. Surfshark's VPN offers access to over 4,500 servers and supports unlimited devices.
Surfshark One differs from other VPN packages by providing essential tools for post-compromise care and customizable security settings. Competitors like ExpressVPN and NordVPN offer tiered pricing structures with advanced security features in higher-tier plans.
To acquire Surfshark One, users can visit the Surfshark website and choose from various subscription plans. The cost difference between the Surfshark Starter plan and Surfshark One is minimal, with Surfshark One starting at .49 per month. Surfshark One+ includes additional features like personal data removal and identity theft coverage.
Only a few providers currently offer both VPN and antivirus capabilities, including Surfshark, Private Internet Access, and CyberGhost.