Microsoft has released optional February updates for Windows 11 versions 25H2 and 24H2, which include several enhancements:
- A network speed test tool accessible from the taskbar for measuring Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and cellular connections.
- Enhanced camera settings with new pan and tilt options for supported cameras.
- A built-in version of the System Monitor (Sysmon) tool, available as an optional feature.
- Improvements to Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) for Windows 11 Arm64 devices.
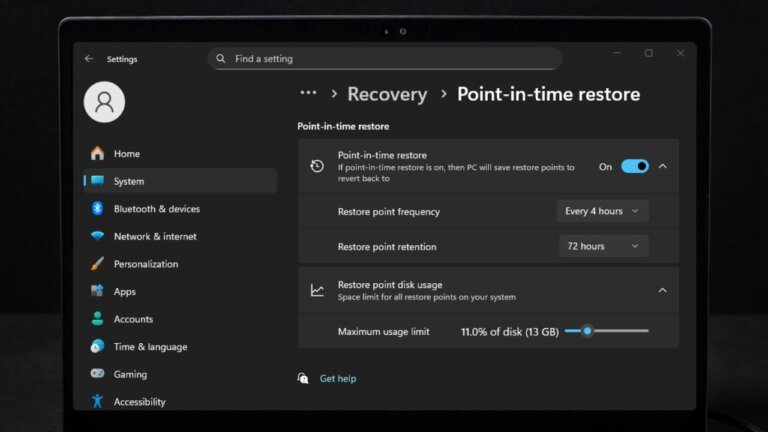
- A new automatic recovery tool for Windows 11 Professional devices not domain-joined.
- Support for .webp images as desktop backgrounds.
- Introduction of new emojis in the Emoji 16.0 release.
- BitLocker improvements to prevent devices from becoming unresponsive after entering a recovery key.
Additionally, Microsoft has shared release notes for an upcoming optional update for Windows 11 version 26H1, which is currently only available to Insiders on the Canary Channel and is expected to debut on new devices with advanced silicon.