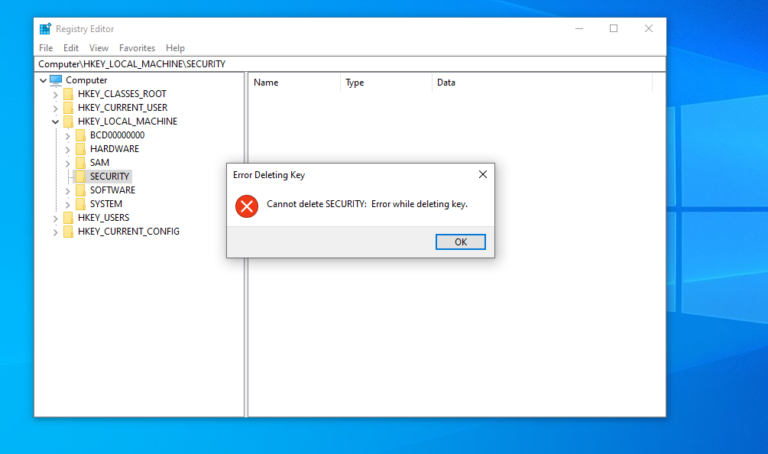
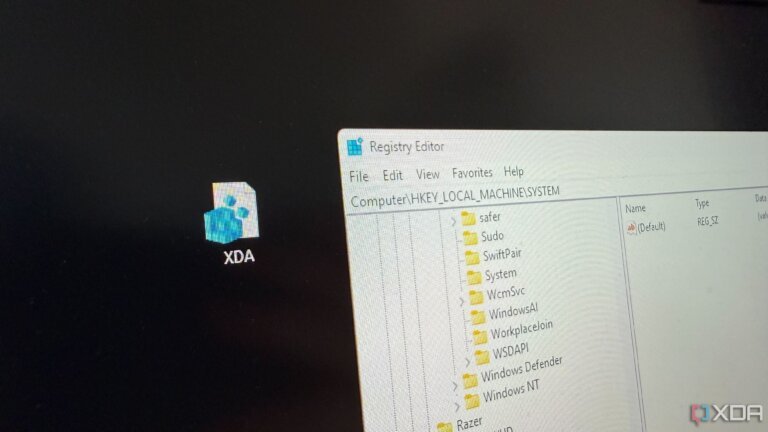
Microsoft will end official support for Windows 10 on October 14, meaning users will no longer receive bug fixes, technical support, or security updates. Extended security updates (ESU) will be available for a fee, primarily aimed at businesses and educational institutions, with a consumer version available for one year. Users can also consider alternative operating systems like Linux or ChromeOS Flex. Microsoft suggests cloud solutions like Windows 365 or Azure Virtual Desktop for those unable to upgrade their devices. Some users are opting for third-party security software, such as the 0patch agent, to address security risks associated with using Windows 10 post-support. There are methods to bypass Windows 11 upgrade compatibility checks using tools like Rufus or Registry Editor modifications.