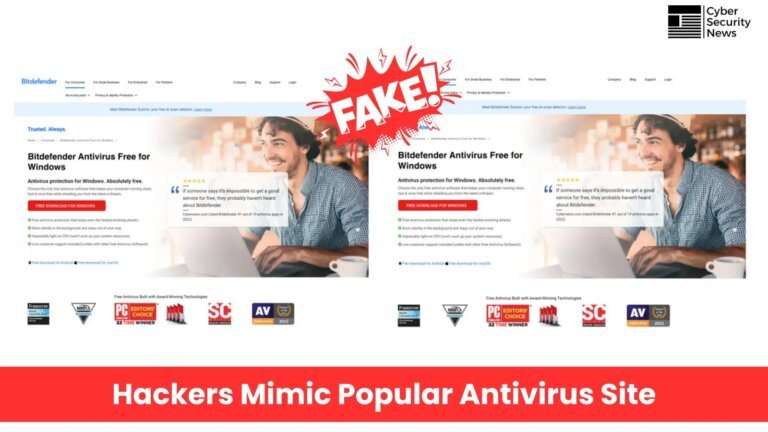
Researchers at DomainTools Investigations (DTI) have identified counterfeit websites mimicking platforms like DocuSign and Gitcode, designed to lure users into downloading malware, specifically a remote access trojan (RAT). These fraudulent sites use tactics such as fake CAPTCHA prompts to enhance credibility and prompt users to download malicious software disguised as necessary updates. The operation employs a multi-stage downloader PowerShell script, reminiscent of older scams that alarmed users with popups about virus infections. Users are advised to be cautious with unfamiliar websites and verify the authenticity of download prompts.