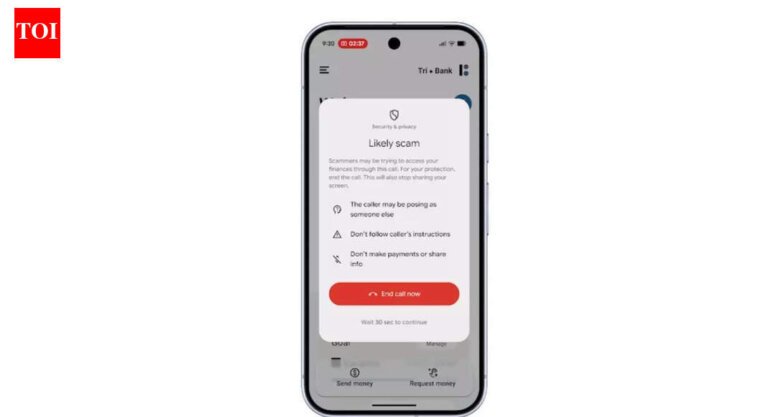
A 63-year-old resident in Solon, Ohio, lost over a million dollars to a scammer posing as a cryptocurrency investment guru. The scam began with a friendly outreach on Facebook, which transitioned to WhatsApp for private conversations. Over several months, the victim was convinced to invest in what he thought was a legitimate opportunity. This incident reflects a broader trend, as the FBI reported that Ohioans aged 60 and older lost over a million to fraud in 2024. Meta Platforms is enhancing tools to detect and disrupt fraudulent activities on its platforms, including new warnings for screen sharing requests on WhatsApp. In the first half of 2025, Meta removed eight million accounts suspected of scams and shut down 21,000 pages impersonating legitimate businesses. Warning signs in the Solon case included initial contact from a stranger, a quick shift to cryptocurrency discussions, and unusually high promised returns.