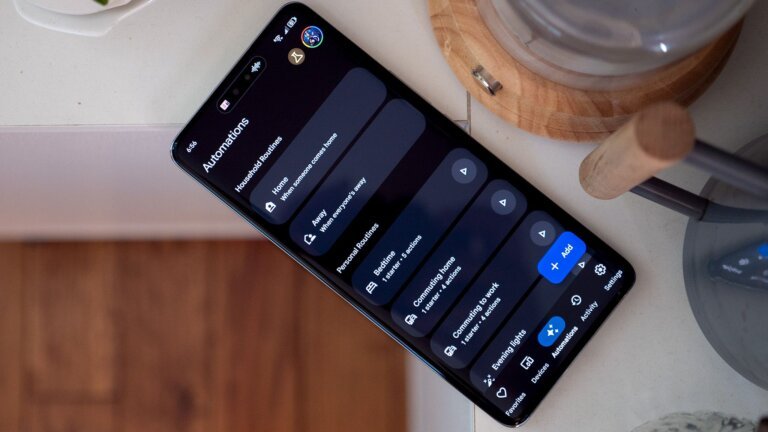
Google Home is implementing significant updates in March, including improvements to the Gemini voice assistant's interaction with smart home devices through room-level commands. Users can now issue commands like "turn off the kitchen," targeting specific devices. The update introduces new automation triggers, such as "Security system is armed" and "Device is plugged in." Google is also expanding its partnership with Yale Smart Lock, allowing users to view lock history and receive notifications through the Google Home app. The Gemini update enhances voice assistant capabilities, utilizing users' home addresses for contextually relevant responses, and improving accuracy for commands related to notes, reminders, calendars, and alarms. Additional features include enhanced responses for informational queries, fewer interruptions during speech, increased reliability for automations, improved accuracy in playing new songs, and a new “Live Search” feature for Google Home Premium subscribers. A software patch for Nest Wifi Pro is also set to enhance security and performance. Gemini for Home was first unveiled in late 2022, with early access starting in October, and users have reported positive experiences with features like "Ask Home."