Windows 11 offers a mix of security and privacy features, with a recommendation for users to opt for a Copilot+ PC with a Qualcomm Snapdragon X-series processor for enhanced security. Most users log in with a Microsoft account, which provides benefits such as two-factor authentication, device-bound passkeys, account recovery options, and automatic disk encryption. However, using a local account poses security risks, including limited recovery options and lack of support for key security features.
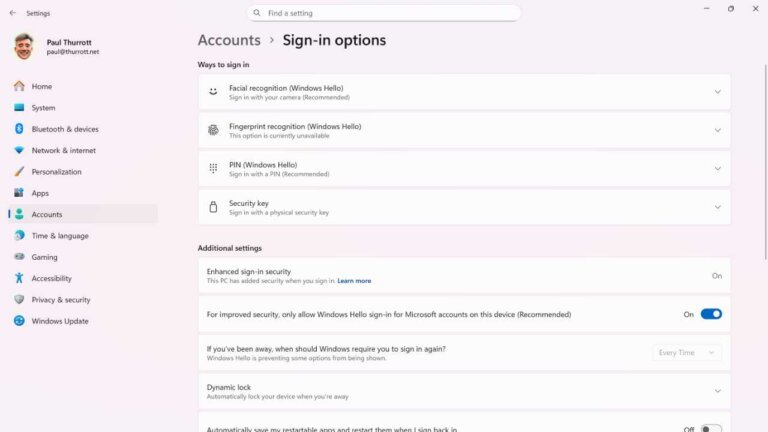
To secure Windows 11, users should take several steps during initial setup or later, including enabling Windows Security features, verifying device encryption, and enhancing sign-in security through Windows Hello options like facial and fingerprint recognition. Additional security features such as Controlled Folder Access and Smart App Control can be configured for better protection. Users are advised to remove unnecessary third-party security apps and keep Windows 11 and installed applications up-to-date to maintain security. Regular updates and proper configuration of Windows Update settings are also essential for preventing disruptions and ensuring data safety.