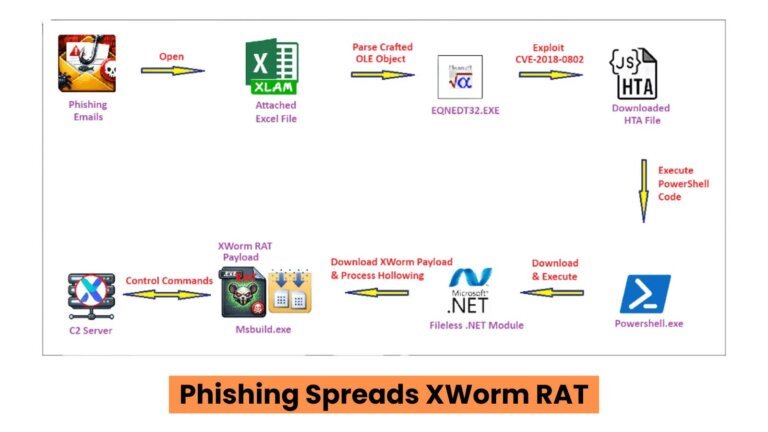
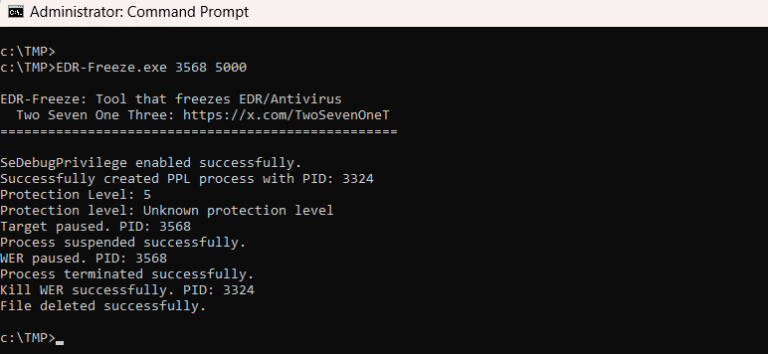
In 2026, cybersecurity has evolved significantly, necessitating organizations to prioritize five critical threats identified by expert Danny Mitchell from Heimdal:
1. AI Vulnerabilities: Attackers can manipulate machine learning models by introducing corrupted data, leading to dangerous decisions by AI systems.
2. Cyber-Enabled Fraud and Phishing: Phishing attacks have become more sophisticated with AI, using deepfake technology to impersonate individuals and evade detection.
3. Supply Chain Attacks: Cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities in software libraries and vendor relationships, compromising trusted software updates and access credentials.
4. Software Vulnerabilities: The rapid discovery of software vulnerabilities outpaces patching efforts, leaving systems exposed to attacks, especially legacy systems.
5. Ransomware Attacks: Modern ransomware employs double extortion tactics, encrypting and stealing data, pressuring businesses to comply with ransom demands.
Mitchell recommends strategies such as auditing AI systems, implementing multi-channel verification, securing supply chains, prioritizing patch management, and developing ransomware response plans to combat these threats.