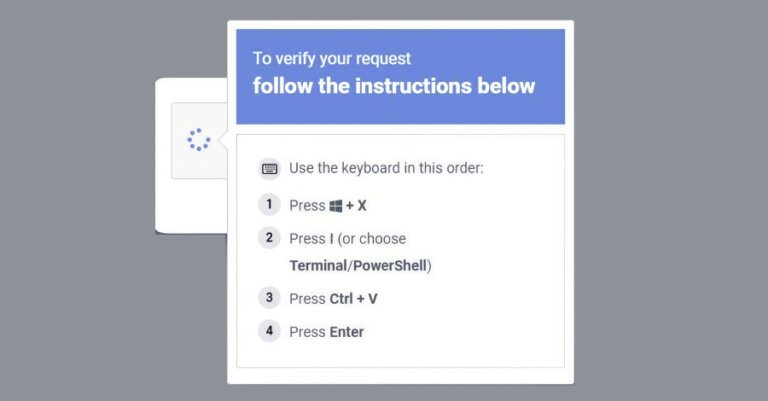
Microsoft revealed a social engineering campaign named ClickFix that exploits the Windows Terminal application to deploy Lumma Stealer malware. Detected in February 2026, this campaign instructs users to access Windows Terminal using the Windows + X → I shortcut, enhancing its perceived legitimacy. Attackers evade detection by manipulating users into executing harmful commands through deceptive prompts. The attack chain involves pasting a hex-encoded command into Windows Terminal, which opens additional Terminal and PowerShell instances, leading to a PowerShell process that decodes a script. This process downloads a ZIP payload containing a renamed 7-Zip binary, which extracts files and initiates a multi-stage attack, including retrieving payloads, establishing persistence, configuring Microsoft Defender exclusions, exfiltrating data, and deploying Lumma Stealer by injecting it into "chrome.exe" and "msedge.exe." Lumma Stealer targets browser artifacts to harvest credentials. A secondary attack pathway involves downloading a batch script that writes a Visual Basic Script to the Temp folder and connects to Crypto Blockchain RPC endpoints, also using QueueUserAPC() for code injection into browsers to extract data.