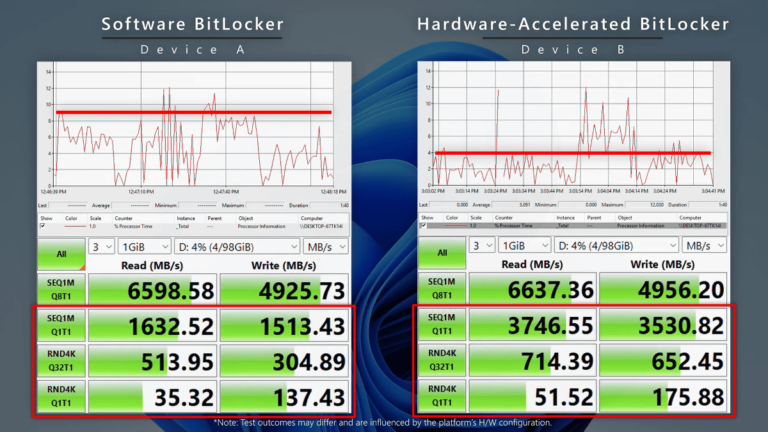
TrigrZolt conducted benchmarks on multiple Windows versions (XP, Vista, 7, 8.1, 10, and 11) using a Lenovo ThinkPad X220. Windows 8.1 had the fastest startup time due to its Fast Boot feature, while Windows 11 was notably slow, struggling to load the taskbar. Windows XP had the smallest installation size and least RAM usage at 800 MB, compared to Windows 11's 3.3 GB. In memory management tests with the Supermium browser, Windows XP and Windows 11 performed similarly under heavy usage, but Windows 7 and 8.1 managed to keep over 200 tabs open before hitting the 5 GB RAM limit. Windows 11 also performed poorly in battery life, video rendering, and application launch times, with users experiencing significant delays. The poor performance of Windows 11 is attributed to extensive code rewrites since Windows 7 and the default storage encryption with BitLocker, which slows performance. Microsoft has implemented workarounds to improve File Explorer's responsiveness. Overall, the trend indicates that increasing resource demands can lead to inefficiencies in software performance.