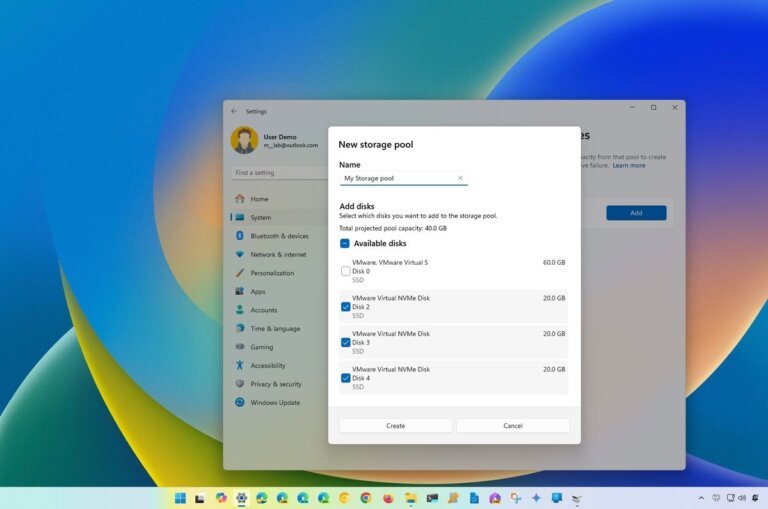
Microsoft's Resilient File System (ReFS) supports volumes up to 35 petabytes and offers robust data protection through checksums and continuous integrity checks, reducing the risk of data corruption. However, Windows 11 defaults to the NTFS file system, requiring users to use command-line tools to access ReFS features, which may deter average consumers. ReFS is primarily designed for Windows Server environments and has not gained popularity among general users. Testing shows that Windows 11 formats new drives as NTFS, making ReFS less accessible. ReFS can experience performance degradation on single-drive consumer PCs compared to NTFS and lacks features like file system compression, encryption, object IDs, and extended attributes, raising compatibility concerns. Microsoft has introduced the Agent Launchers framework for AI agent registration in Windows, amidst user backlash regarding the evolution of Windows into an "agentic OS." The Windows and Devices segment generated .3 billion in the last fiscal year, remaining flat over three years, while Gaming and LinkedIn generated higher revenues. Users have reported frequent feature changes and declining quality in Windows 11, with Microsoft's Controlled Feature Rollout system causing inconsistencies across devices. ReFS is accessible through the Dev Drive feature in Windows 11, which prioritizes performance over security. Microsoft faces competition from various fronts, including Valve's SteamOS, Apple's upcoming MacBook, and Google's Chrome OS, particularly in the education sector.