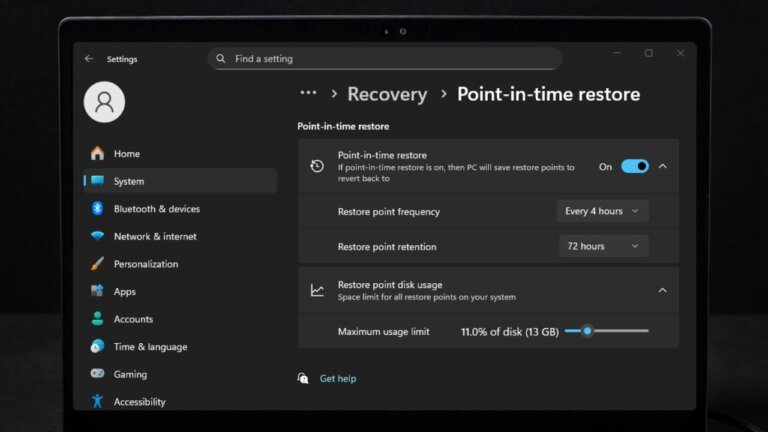
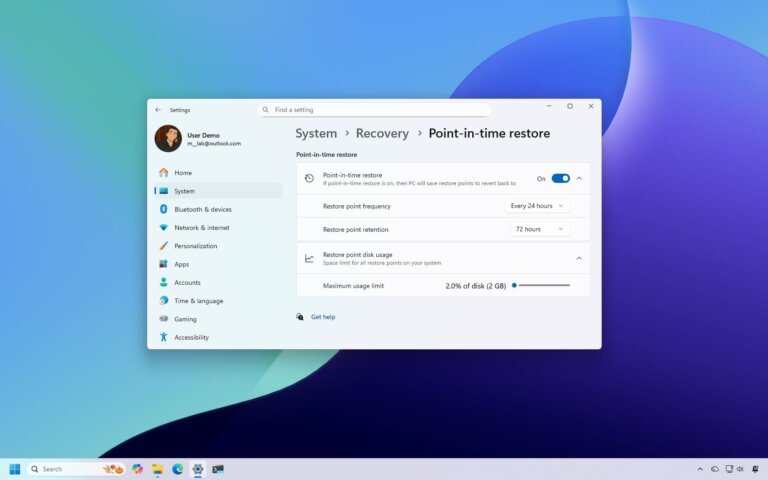
Microsoft's Copilot AI has received mixed reviews from users, with many preferring a more reliable operating system over new AI features. Users have reported inaccuracies in Copilot's responses and raised concerns about privacy and resource consumption. To disable or remove Copilot in Windows 10 and 11, users can access Task Manager, navigate to Startup apps, and disable Copilot. Additionally, tools like "Remove Windows AI" and "Flyoobe" can help manage AI components, with the latter allowing users to disable specific AI settings after installation.