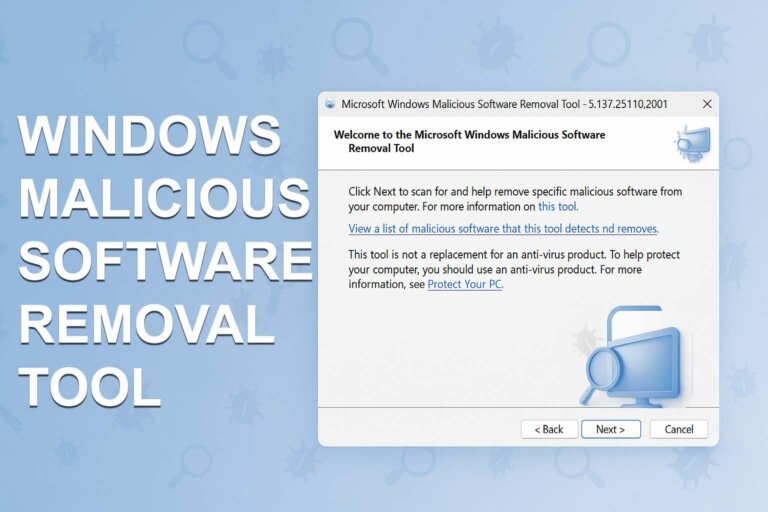
The Windows Malicious Software Removal Tool (MSRT) identifies and eliminates specific high-risk malware families on Windows devices. It is updated monthly by Microsoft and is integrated into all supported versions of Windows 10 and Windows 11. MSRT functions as a cleanup utility, scanning for known active malware infections. Users can run the tool manually by pressing Windows + R, typing mrt, and selecting a scan type. MSRT is recommended for use after installing software from unfamiliar sources, when a PC shows unusual behavior, for quick secondary scans, or in response to Windows Defender alerts. Manual downloads of MSRT are available for offline systems. The tool maintains a detailed log of scans in the Debug folder. MSRT targets malware such as MyDoom, Blaster, and Sasser, and while it removes infections, it does not provide real-time monitoring. Microsoft updates the tool monthly, and it runs automatically after updates but can also be launched manually.