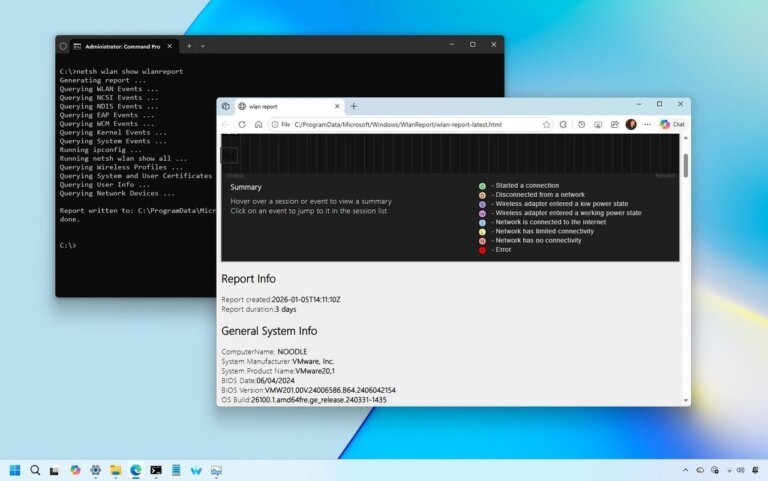
Linux Mint 22.3 (Zena) has been released as a stable build after beta testing. It features an upgraded Cinnamon 6.6 desktop environment, which includes a redesigned application menu with a sidebar, smaller categories, and hideable elements. The update also includes audio improvements, new system icons, better troubleshooting tools, and the ability to pause TimeShift snapshots.