Albiriox is an Android malware identified as a sophisticated tool targeting financial applications, primarily affecting users in Austria. It operates as malware-as-a-service (MaaS), allowing cybercriminals to conduct on-device fraud through remote control and screen manipulation. Albiriox uses deceptive tactics, such as fake applications and dropper APKs, to infiltrate devices and exploits Android’s accessibility services for extensive control. It is linked to Russian-speaking developers and is promoted on underground forums, with subscriptions starting at [openai_gpt model="gpt-4o-mini" prompt="Summarize the content and extract only the fact described in the text bellow. The summary shall NOT include a title, introduction and conclusion. Text: In the realm of cybersecurity, a new threat has emerged that is capturing the attention of experts and financial institutions alike. Albiriox, an Android malware, has been identified as a sophisticated tool targeting financial applications with alarming precision. This malware-as-a-service (MaaS) offering enables cybercriminals to execute on-device fraud through remote control and screen manipulation, posing significant risks to users primarily in Austria, but with implications that could extend globally.
How Albiriox Evades Detection and Spreads
Albiriox employs a variety of deceptive tactics to infiltrate devices, including the use of fake applications and dropper APKs that mimic legitimate software. Once installed, it exploits Android’s accessibility services to gain extensive control over the device, allowing attackers to manipulate screens and extract sensitive information without the user's awareness. Security experts have traced its origins to Russian-speaking developers who promote this malware on underground forums, offering subscriptions that start at 0 per month.
The malware’s distribution is further facilitated by phishing campaigns and counterfeit Google Play Store pages, which lure unsuspecting users into downloading infected APKs. Upon installation, Albiriox requests permissions under the guise of system updates or essential features, preying on users' trust in routine prompts. Researchers highlight its versatility, as it targets a wide array of applications, from major banking platforms to cryptocurrency wallets.
The Technical Underpinnings of On-Device Fraud
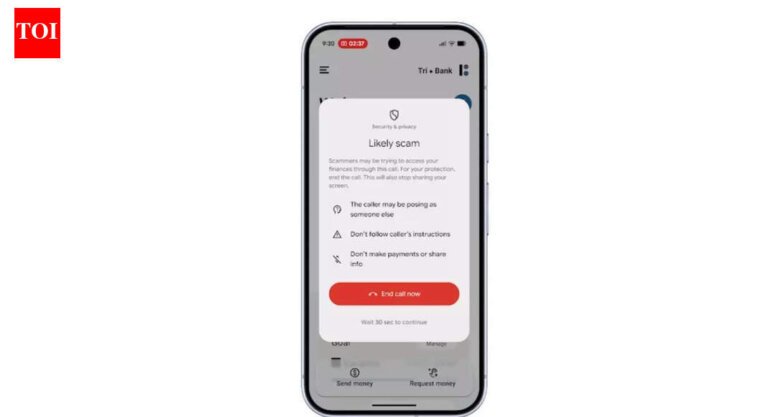
Delving into its technical aspects, Albiriox merges remote access trojan (RAT) functionalities with overlay attacks, creating a hybrid threat particularly effective against mobile banking. Utilizing Telegram bots for command-and-control communications, it exfiltrates stolen data such as login credentials and two-factor authentication codes. One of its notable features is the ability to perform real-time screen manipulation, enabling attackers to simulate user actions and authorize fraudulent transactions seamlessly.
Moreover, Albiriox can disable security features on devices, including antivirus scanners and app permissions, ensuring its persistence. Analysis indicates that it targets over 400 apps, demonstrating a calculated focus on financial institutions worldwide.
Links to Russian Cybercrime Networks
Evidence suggests that Albiriox has ties to Russian cybercrime networks, with promotional materials and discussions conducted in Russian. Security firms have observed its development, noting similarities to other Eastern European malware families. The malware's affordability and user-friendly design have led to its rapid adoption among cybercriminals, raising alarms within the cybersecurity community.
Industry insiders speculate that Albiriox may be an evolution of previous malware like BlackRock, which targeted social and financial applications. This progression indicates a maturing ecosystem where threats build upon one another, incorporating lessons learned from past detections to enhance stealth.
Impact on Users and Financial Institutions
Victims of Albiriox face not only financial losses but also significant privacy breaches, as the malware can access personal messages, contacts, and location data. In Austria, where initial campaigns have been concentrated, banks have reported an uptick in unauthorized transactions linked to mobile compromises. Financial institutions are responding by bolstering app security with advanced measures such as behavioral analytics and device fingerprinting, yet the malware's ability to exploit accessibility features presents ongoing challenges.
Experts recommend that users enable two-factor authentication, refrain from sideloading apps, and keep their devices updated to mitigate risks. The broader implications of Albiriox's rise could lead to a decline in consumer trust in mobile banking, potentially driving a shift towards more secure, hardware-based solutions or biometric-only authentications.
Comparative Analysis with Past Threats
When comparing Albiriox to predecessors like Joker malware, which infected apps via Google Play, it is evident that advancements have been made in persistence and fraud execution. While Joker focused primarily on billing fraud, Albiriox emphasizes on-device control, making it more akin to RATs typically seen in desktop environments. Historical analyses reveal a pattern of escalating sophistication, with Albiriox integrating VNC capabilities that allow attackers to observe and intervene in real time.
Strategies for Mitigation and Future Defenses
To combat the threat posed by Albiriox, cybersecurity firms advocate for multi-layered defenses. Although Google has enhanced Play Store vetting processes, sideloading remains a significant vulnerability. Users are encouraged to scrutinize app permissions, particularly those requesting accessibility services, which can be indicative of malware.
Enterprises are investing in mobile threat defense solutions that can detect anomalous behaviors, such as unexpected screen streaming or permission escalations. Collaboration between app developers and security researchers is essential, as demonstrated by successful takedowns of similar MaaS operations.
The Broader Ecosystem of Mobile Threats
Albiriox is not an isolated incident; it exists within a thriving underground market where malware is commoditized. Forums advertise it alongside tools for phishing and social engineering, creating a comprehensive toolkit for cybercriminals. The malware’s pricing structure, set at 0 per month, makes it accessible to smaller operators, thereby increasing the risk of sophisticated attacks being executed by less experienced individuals.
Case Studies and Real-World Incidents
While specific victim accounts remain scarce due to privacy concerns, aggregated data from threat intelligence firms illustrate a troubling trend. Reports from Austrian users indicate unauthorized crypto transfers after downloading seemingly benign applications, later traced back to Albiriox droppers. Similar patterns have emerged in analyses, where infected devices facilitated significant financial losses.
Expert Insights and Industry Response
Cybersecurity professionals describe Albiriox as a “masterclass in mobile mischief,” seamlessly blending RAT and overlay techniques. Their analyses reveal how it deceives users into granting permissions by faking system updates, a tactic that has successfully fooled even the most discerning individuals. Industry groups are advocating for standardized reporting of mobile threats to facilitate faster intelligence sharing.
Navigating the Future of Mobile Security
The emergence of Albiriox signifies a shift towards more interactive, real-time fraud methods in mobile malware. With its sights set on over 400 applications, it poses a systemic risk to the financial sector, prompting calls for international cooperation to track and dismantle MaaS providers. Innovations such as AI-driven anomaly detection could serve as a protective measure, analyzing app behaviors in real time. Meanwhile, users must adopt a security-first mindset, treating every download with the utmost caution." max_tokens="3500" temperature="0.3" top_p="1.0" best_of="1" presence_penalty="0.1" frequency_penalty="frequency_penalty"] per month. The malware spreads through phishing campaigns and counterfeit Google Play Store pages, requesting permissions under the guise of system updates.
Albiriox combines remote access trojan (RAT) functionalities with overlay attacks, utilizing Telegram bots for command-and-control communications and exfiltrating sensitive data like login credentials. It can disable security features on devices and targets over 400 applications, including banking platforms and cryptocurrency wallets. Victims face financial losses and privacy breaches, with banks in Austria reporting unauthorized transactions linked to mobile compromises. Cybersecurity experts recommend enabling two-factor authentication and avoiding sideloading apps to mitigate risks.
Albiriox represents an evolution of previous malware, integrating advanced techniques for persistence and fraud execution. It exists within a broader underground market where malware is commoditized, making it accessible to less experienced cybercriminals. Reports indicate unauthorized crypto transfers traced back to Albiriox, highlighting its impact on users. Cybersecurity professionals describe it as a blend of RAT and overlay techniques, emphasizing the need for standardized reporting and international cooperation to combat such threats.