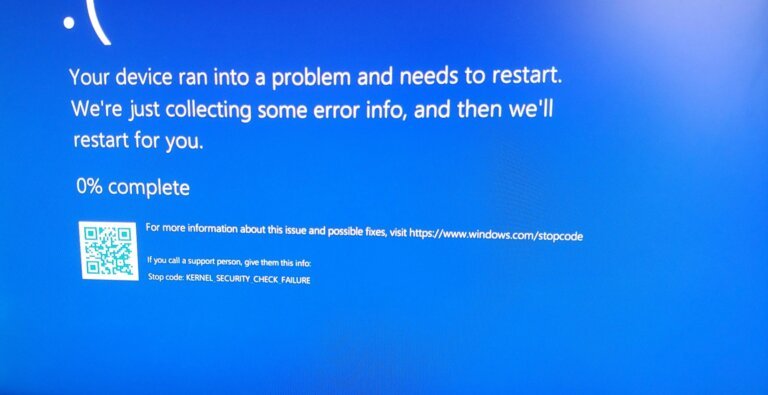
YouTube experienced a significant outage affecting its services, including YouTube Music, YouTube Kids, and YouTube TV, primarily due to issues with its recommendations system. Downdetector recorded 300,000 to 350,000 user reports in the U.S. and numerous complaints globally. By late evening, YouTube confirmed that full service was restored across all platforms, and no videos or accounts were deleted during the disruption. YouTube's engineers are expected to investigate the cause of the failure to prevent future occurrences.