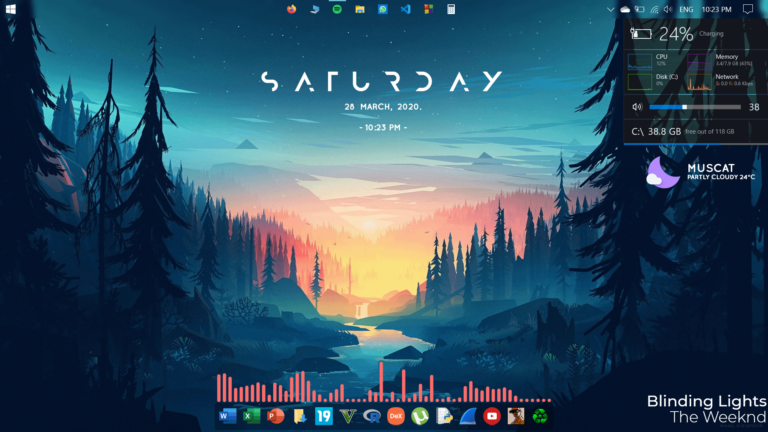
Rainmeter is a free and open-source software for Windows 11 that allows users to customize their desktop with a variety of skins, plugins, and effects. It has a vast library of skins available on platforms like DeviantArt and Rainmeter subreddits. Users can enhance functionality by incorporating plugins, which are dynamic link library (.dll) programs. The official Rainmeter site provides tips and tricks for both novice and experienced users, including guides on coding variables and using the WebParser plugin. The open-source nature of Rainmeter allows users to make extensive code adjustments for further customization. Rainmeter's lightweight design ensures that customizations do not compromise system performance.