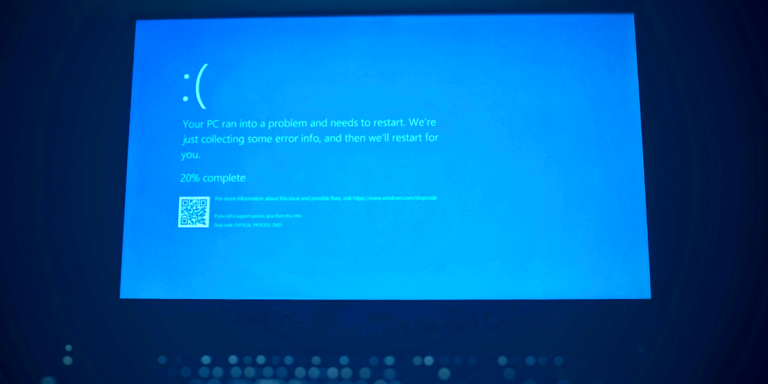
The Windows 11 24H2 update has caused complications, leading Microsoft to compile a list of affected hardware and software along with potential fixes. Users experiencing crashes can try the following solutions:
1. Remove Windows Hello: Users with laptops that have integrated cameras may experience system freezes. To fix this, navigate to Settings > Accounts > Sign in options, expand the Facial Recognition section, and click Remove. Optionally, remove fingerprint and PIN settings and set up a password.
2. Change Registry Settings for SSDs: The update has made certain SSDs from Western Digital and SanDisk incompatible. A temporary fix involves modifying the registry. Open the Registry Editor, navigate to ComputerHKEYLOCALMACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlStorPort, locate or create the DWORD HmbAllocationPolicy, modify its value to 0 or 2, and restart the PC.
3. Perform Windows Updates Again: Subsequent updates may resolve existing issues. Check for updates in Windows Update, download all related to the 24H2 version, and restart the PC as necessary.
4. Reroll Windows 11: Users can revert to the previous version within 10 days of the update if the option is available. Go to Settings > System > Recovery and select Go back. If the option is greyed out, users can download Windows 11 23H2 from Microsoft’s website for a clean installation, ensuring to back up data first.