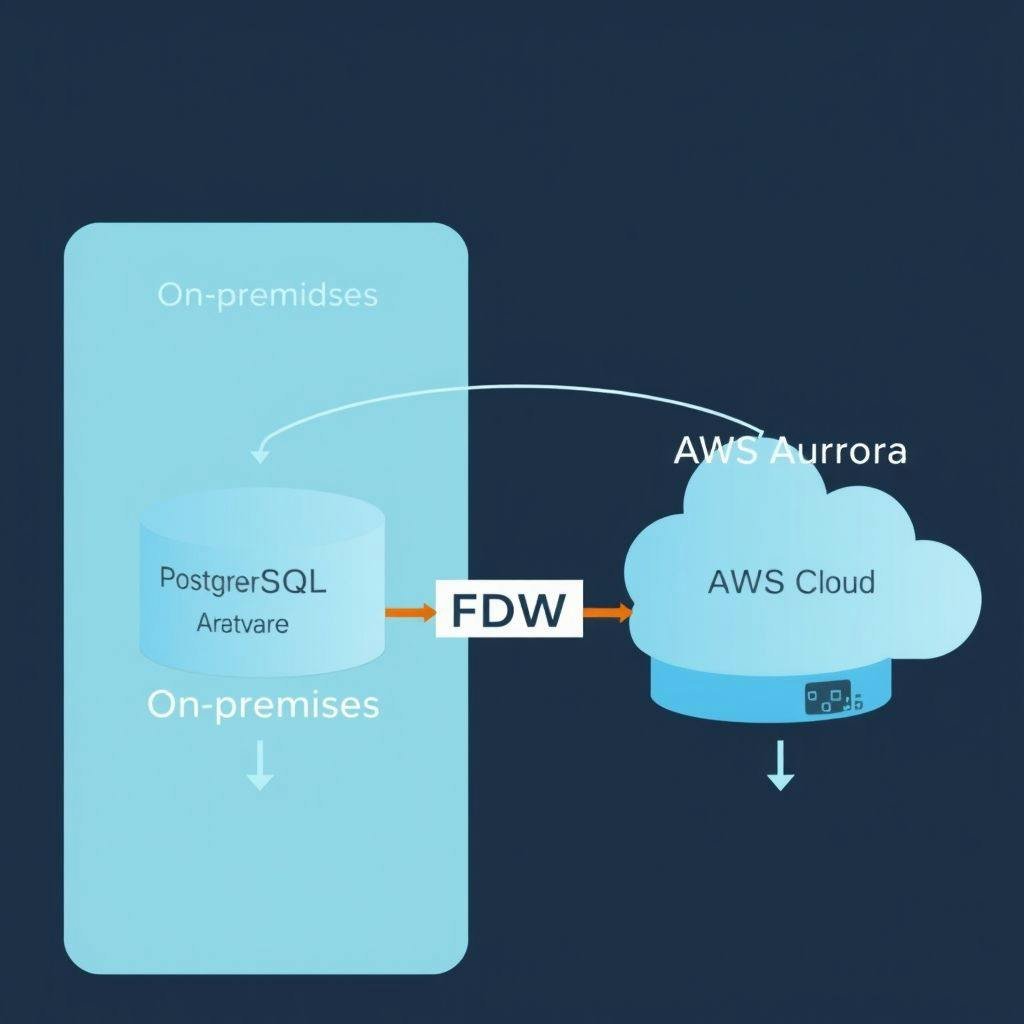
Creating a Foreign Data Wrapper in PostgreSQL and Aurora PostgreSQL on AWS RDS
In the realm of database management, the ability to seamlessly access and manipulate data from external sources is a game-changer. Foreign data wrappers (FDWs) serve as a vital conduit for PostgreSQL and Aurora PostgreSQL, enabling users to interact with data stored across various systems without the cumbersome task of data migration. This functionality is particularly beneficial for organizations that rely on multiple databases, allowing them to leverage disparate data sources efficiently.
Imagine a scenario where a company utilizes PostgreSQL as its primary transactional database while needing to analyze sales data housed in a separate SQL database. By employing a foreign data wrapper, the organization can facilitate real-time analysis, bridging the gap between these two systems effortlessly. The integration not only enhances data accessibility but also streamlines analytical workflows.
Setting Up a Foreign Data Wrapper
Prerequisites
To embark on this journey, ensure you have access to your PostgreSQL or Aurora PostgreSQL instance on AWS RDS. Additionally, your user account must possess the necessary privileges to create extensions and manage data wrappers.
Step 1: Install the Foreign Data Wrapper
Once connected to your PostgreSQL database, the first step is to install the desired FDW. For instance, if you wish to set up a PostgreSQL FDW, execute the following SQL command:
CREATE EXTENSION postgres_fdw;The process is similar for Aurora PostgreSQL. The default FDW for accessing remote PostgreSQL instances is postgres_fdw, although you may explore other wrappers tailored to your specific needs.
Step 2: Set Up Foreign Data Wrapper Access for Public and Current Users
After installing the FDW, it’s essential to configure the necessary permissions. To allow public access for readability, execute:
GRANT USAGE ON FOREIGN SERVER foreign_server_name TO PUBLIC;For a more controlled approach, you can specify privileges for individual users or roles. Here’s how to grant usage to a specific user:
GRANT USAGE ON FOREIGN SERVER foreign_server_name TO username;Step 3: Create a Foreign Server
The next step involves creating the foreign server that your FDW will connect to. This can be achieved with the following SQL command, ensuring to replace foreign_server_name and hostname with your specific details:
CREATE SERVER foreign_server_name
FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER postgres_fdw
OPTIONS (host 'hostname', dbname 'dbname', port '5432');Step 4: Create User Mapping
User mapping is essential for establishing the authentication details of the foreign server. To create a user mapping, utilize the following command:
CREATE USER MAPPING FOR local_username
SERVER foreign_server_name
OPTIONS (user 'remote_username', password 'remote_password');Step 5: Create Foreign Tables
With the foreign server and user mapping established, you can now create foreign tables that reference the remote tables. For instance, if you have a remote table named remote_table, execute:
CREATE FOREIGN TABLE remote_table (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
data VARCHAR(50)
)
SERVER foreign_server_name
OPTIONS (table_name 'remote_table');Use Case:
Consider an online retailer that operates a PostgreSQL database for its core operations while utilizing an external SQL database to track customer feedback. By implementing a foreign data wrapper, the retailer can efficiently integrate customer feedback directly into their analytics. This integration allows for real-time insights into customer satisfaction, enabling the retailer to adjust marketing strategies and enhance product offerings based on live customer responses.
Incorporating foreign data wrappers enhances database capabilities, streamlining workflows for developers and data analysts alike. Whether integrating disparate systems or maintaining broader access to data resources, mastering FDWs is an invaluable asset in the database management toolkit.