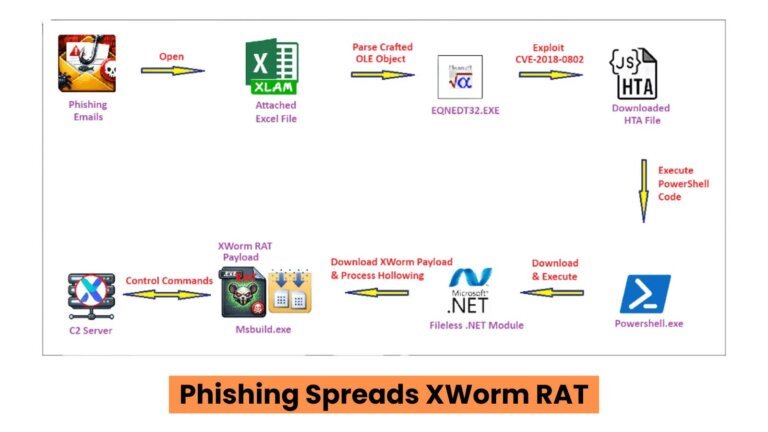
Cofense Intelligence reported that threat actors are exploiting Windows File Explorer and WebDAV servers to deliver Remote Access Trojans (RATs) to corporate systems, bypassing browser security measures. This method allows attackers to infiltrate machines without using web browsers, taking advantage of File Explorer's ability to connect to remote WebDAV servers. Despite WebDAV being deprecated by Microsoft in November 2023, it is still supported in Windows, creating a vulnerability. The campaigns began in February 2024, with a significant increase in September 2024, and 87% of these campaigns deliver multiple RATs, including XWorm, Async RAT, and DcRAT. Victims typically receive phishing emails disguised as invoices, containing URL or LNK shortcut files that initiate a WebDAV connection. The attacks often utilize Cloudflare Tunnel for hosting malicious WebDAV servers, making the traffic appear legitimate. Notably, 50% of affected campaigns are in German, while 30% are in English. The report emphasizes the risks posed to individuals holding digital assets, as RATs can access sensitive information, including crypto wallet files. Organizations are advised to monitor network traffic for Cloudflare Tunnel instances and educate users about the risks associated with File Explorer's capabilities.