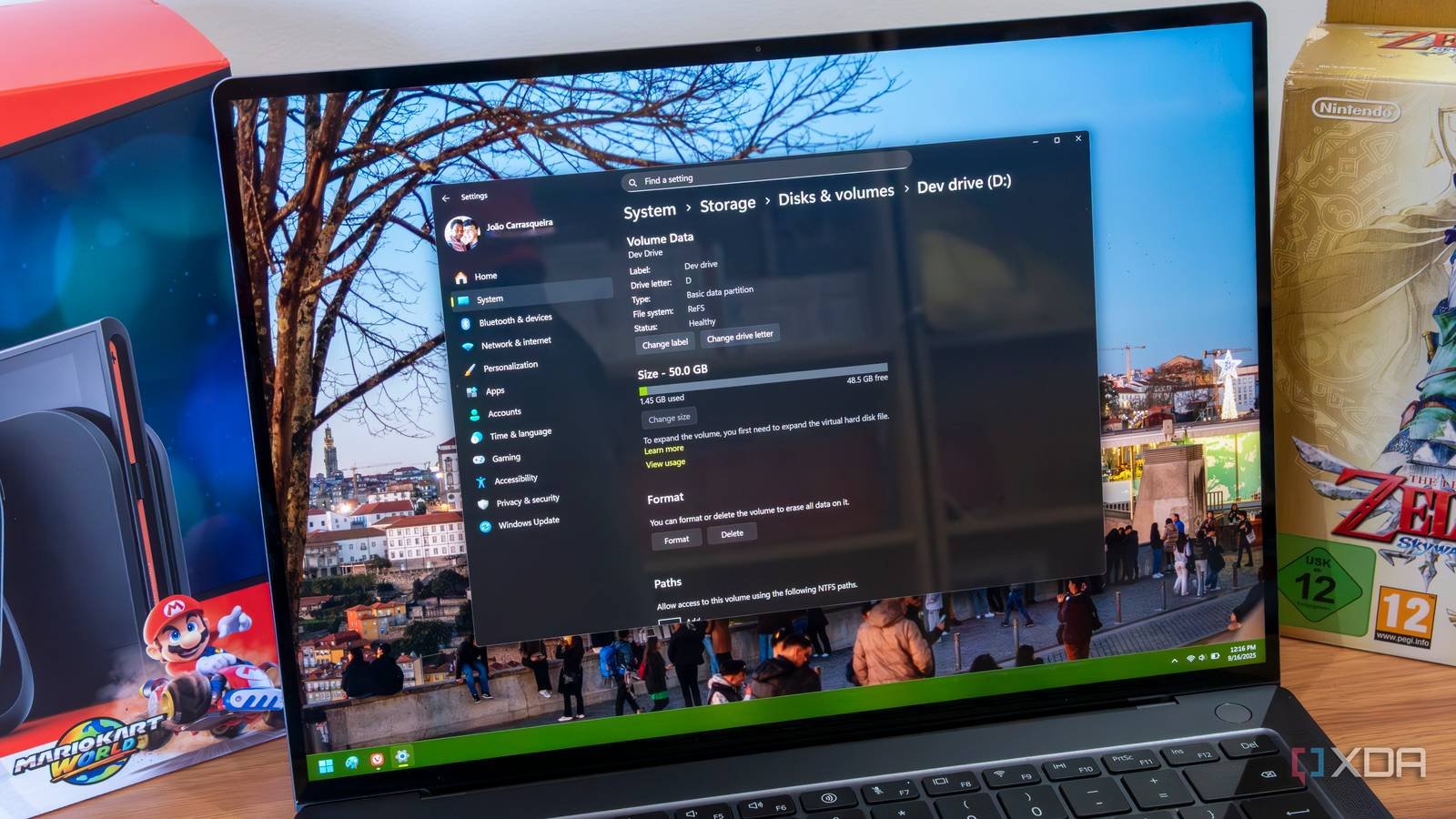
Windows 11 introduces a variety of features that may go unnoticed by many users, yet one particularly noteworthy addition is the Dev Drive. This innovative storage volume is tailored specifically for developers, offering enhancements that can significantly boost productivity.
It’s faster
Some notable improvements
Dev Drives stand apart from conventional storage options on your computer. Utilizing Microsoft’s ReFS file system, they come equipped with targeted optimizations aimed at enhancing performance for the files stored within. Notably, they support a limited form of copy-on-write functionality, which accelerates write operations. A significant advantage of Dev Drives is their compatibility with Microsoft Defender, allowing the anti-malware solution to operate in “performance mode.” This means that Defender will not continuously scan every file on the drive, resulting in notably faster read and write speeds.
According to Microsoft’s own testing, Dev Drives can deliver performance improvements of up to 41% across various development projects. For instance, when cloning the NodeJS repository locally, users can experience this 41% performance boost. Even in scenarios where the improvement is less pronounced, such as building OrchardCore with DotNet, a 22% enhancement translates to roughly a minute saved in build time—an invaluable advantage for developers striving for efficiency.
It’s secure
As long as you know what you’re doing
While the reduced scanning by Microsoft Defender may raise concerns regarding security, it’s essential to understand that Dev Drives are not intended to replace your primary hard drive. Microsoft recommends using Dev Drives exclusively for storing source code repositories, project files, package caches, and build outputs. Essentially, they should only contain files generated by you or trusted sources during development, avoiding the storage of typical downloaded files or installed applications.
By adhering to these guidelines, developers can mitigate security risks. While a heightened level of caution is necessary compared to standard drives, developers are generally well-versed in best practices for maintaining security.
Flexible and portable
Choose your preferred approach
Dev Drives also offer flexibility in their creation. Developers can opt for two methods: establishing a Dev Drive on a physical partition for slightly improved performance or utilizing a virtual hard drive (VHD) for greater flexibility. The physical partition approach allows for direct interaction with the disk, enhancing speed but limiting mobility. Conversely, creating a Dev Drive on a VHD introduces a virtual layer that, while marginally slower, offers dynamic resizing based on actual storage usage and portability, enabling developers to transfer their work seamlessly to other PCs.
Although Microsoft advises against using a Dev Drive on a different PC after moving it, the ability to transfer data remains a significant advantage. However, it is crucial to remember that Dev Drives are designed for specific purposes. Attempting to repurpose them for general use in pursuit of speed can expose users to unnecessary risks, particularly if it involves disabling protective measures from Microsoft Defender.
Just be careful what you use it for
While the benefits of Dev Drives are clear, they are intended for a defined purpose. Developers should refrain from using them for non-development-related tasks that could compromise security. If you are confident in the trustworthiness of the files you store on a Dev Drive, you might consider leveraging its speed for broader applications, but this carries inherent risks. Ultimately, for developers, the advantages of Dev Drives can lead to substantial productivity gains, solidifying their value within the Windows 11 ecosystem.