Windows continues to house a variety of legacy utilities that serve essential functions for users. While some of these tools, such as Paint3D and the People app, face removal or deprecation, others, like the classic Control Panel, are expected to remain for the foreseeable future. However, the migration of Control Panel items to the Settings app is still a work in progress. Amidst these changes, one utility stands out for its reliability: Disk Cleanup.
You Can Reclaim Gigabytes Worth of Drive Space
Disk Cleanup remains a valuable tool for Windows 11 users, especially when compared to the more automated Storage Sense feature. While Storage Sense operates as a “set-it-and-forget-it” solution for disk management, Disk Cleanup allows for manual operation, providing users with the ability to reclaim significant storage by removing old Windows Update files.
Remove Unnecessary Windows Update Files
Running Disk Cleanup is a straightforward process. Users can launch it, select the items they wish to remove, and watch as space is freed up. However, there’s a trick to maximize this utility: when upgrading your system, Windows retains copies of the previous version, which can take up substantial space. If you’re confident that you won’t need these files for a rollback, you can safely delete them to reclaim valuable gigabytes.
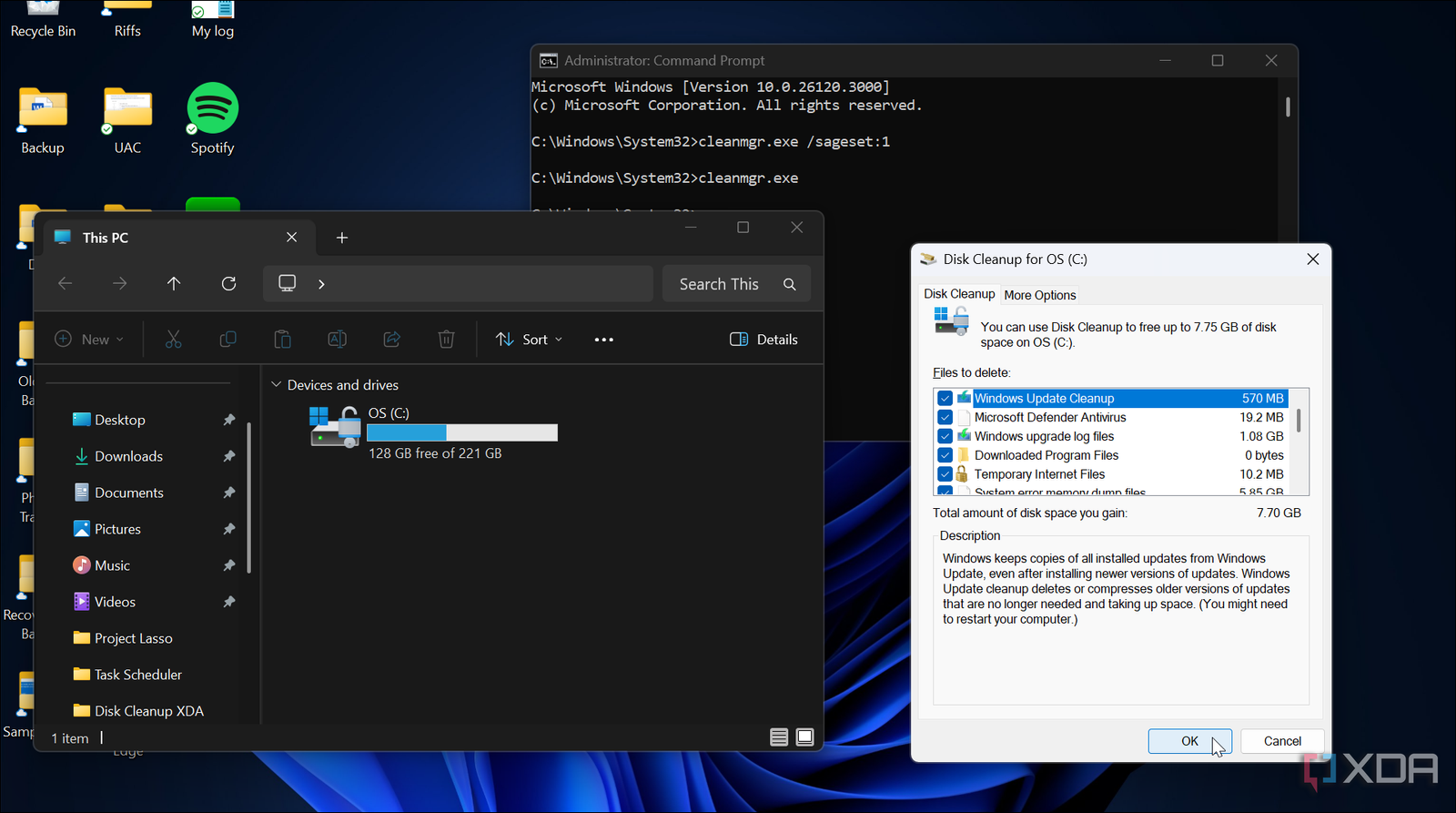
Note that in Windows 11, Disk Cleanup can no longer be accessed directly from the disk properties dialog. Instead, it can be launched via the Run dialog or by searching in the Start menu.
To initiate a cleanup, press Win + R to open the Run dialog, type cleanmgr, and hit Enter. Once Disk Cleanup opens, it will display the amount of disk space that can be cleared by selecting various items, including cache and the Recycle Bin. The more items you select, the more space you can recover. Additionally, clicking the Clean up system files button reveals options for unnecessary update files, potentially allowing users to reclaim several gigabytes of space.
You Know How It Works
It’s a Familiar Utility
For long-time Windows users, Disk Cleanup is a well-known tool, essential for managing limited storage on older PCs. This remains true today, particularly for users engaged in resource-intensive activities such as gaming or video production. The Cleanup recommendations provided by Storage Sense often lack depth and speed, listing only a few files that may not significantly impact available space. In contrast, Disk Cleanup offers a comprehensive view of all removable items, making it a faster and more efficient option.
You Can Make It Run Automatically
Create an Automated Task
While Storage Sense operates automatically, users can also set up Disk Cleanup to run on a schedule using Task Scheduler. This allows for regular maintenance without manual intervention. To create an automated task, follow these steps:
- Open the Command Prompt as Administrator.
- Type cleanmgr.exe /sageset:1 and press Enter.
- When Disk Cleanup opens, select the items you want to clean up each time it runs.
- Open Task Scheduler, create a basic task, and set the desired schedule (weekly, monthly, etc.).
- Select Start a program in the “Action” section.
- In the “Program/script” field, enter: C:Windowssystem32cleanmgr.exe.
- In the “Add arguments” field, type: /sagerun:1 and complete the wizard.
Disk Cleanup is a Better Utility
A More Precise and User-Friendly Tool
Disk Cleanup provides a more user-friendly interface for eliminating unnecessary files compared to navigating through the Settings app for Storage Sense. It quickly identifies and lists items that can be removed, offering users greater control over their storage management. This utility not only runs faster but also allows for significant space recovery without the need for third-party applications.
As Microsoft continues to evolve its operating system, there are whispers of potentially deprecating Disk Cleanup. Should this occur, it will be essential for Storage Sense to enhance its features and usability to meet user needs effectively. For now, Disk Cleanup remains the go-to solution for reclaiming storage space on Windows 11, proving its enduring value in the digital landscape.