Windows 11 introduces a streamlined approach to text file management with the Microsoft Edit tool, which allows users to edit text files directly within Command Prompt or PowerShell. This utility, reminiscent of popular Linux command-line editors like Nano and Vim, is compact, weighing in at under 250KB. Below, we delve into the essential steps to get started with Microsoft Edit.
<h2 class="article-bodysection” id=”section-how-to-use-microsoft-edit-on-windows-11″>How to use Microsoft Edit on Windows 11
Microsoft now includes the Edit command-line tool with the latest version of Windows 11. However, if it’s not pre-installed on your device, you can easily install it manually.
Installation
To install Microsoft Edit on Windows 11, follow these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select Run as administrator.
- Type the following winget command to install Microsoft Edit and press Enter: winget install –id Microsoft.Edit
For those who prefer to obtain Microsoft Edit from GitHub, the open-source tool is also available on the official release page. Download the latest version’s zip file, extract it, and run edit.exe to launch the application. Note that manual configuration is necessary if you choose this route, which involves placing the edit.exe file in a new folder and creating the environment variable. For simplicity, using the Windows Package Manager (winget) is recommended.
Usage
The usage of Microsoft Edit is straightforward:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt and right-click the top result.
- (Option 1) Type this command to launch Microsoft Edit and press Enter: edit
- (Option 2) Type this command to launch the Edit command-line tool as an administrator and press Enter: sudo edit
- Quick note: If you need to edit a text file that requires higher privileges, you can also start the Command Prompt as an administrator.
Once launched, you can manage existing or new files effortlessly.
Opening a file
To edit an existing text file, use the command: edit filename.txt. You can also specify the path by typing: edit c:pathfilename.txt. Alternatively, launch the editor first by typing edit, then navigate to File, select Open File, and choose your desired text file.
Creating a file
To create a new text file, simply use the command: edit filename.txt. You can also create a file within the editor by typing edit, then selecting File and choosing New File.
Editing a file
While using Microsoft Edit, you will find basic text editing options available. The Edit menu provides functionalities such as undo, redo, cut, copy, and paste. Additionally, the find and replace feature is readily accessible.
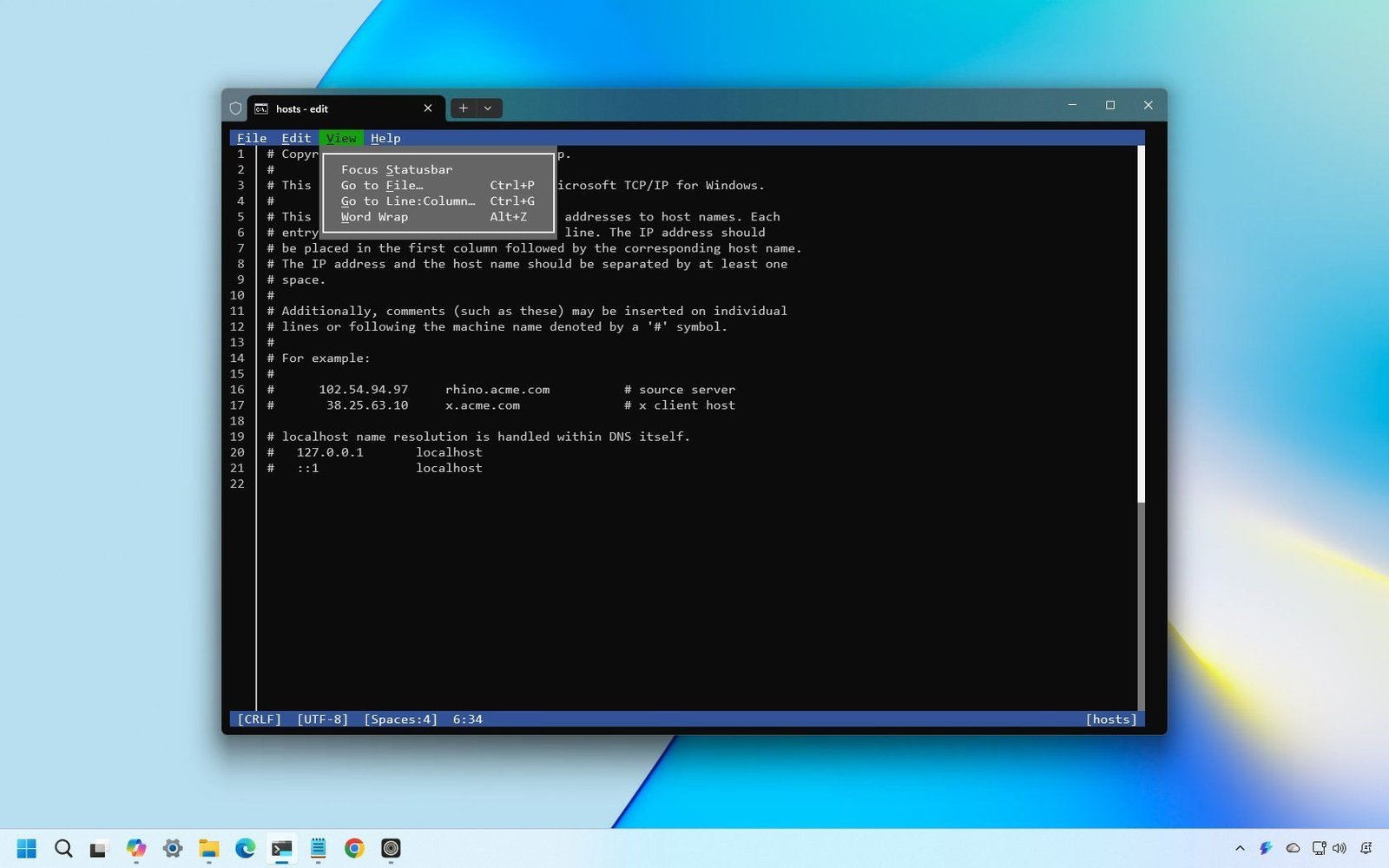
In the View menu, you can manage settings like Word Wrap, control the status bar, and switch between text files.
Saving a file
After completing your edits, use the “Ctrl + S” shortcut to save your work, or navigate to the File menu to select Save or Save As. To exit the editor, you can use the “Ctrl + Q” shortcut or choose Exit from the File menu.
For convenience, the “Esc” key can dismiss menus or UI elements, and most actions have keyboard shortcuts that can be learned within the menus. All shortcuts begin with “Ctrl+”, except for the Word Wrap feature, which uses “Alt + Z”.
Microsoft Edit does not aim to revolutionize text file editing; rather, it serves as a native text editor integrated into Command Prompt and PowerShell, minimizing the need to switch applications. As Notepad evolves with new features, including AI integrations, Microsoft Edit stands as a lightweight alternative focused on basic, distraction-free text editing.
<h3 class="article-bodysection” id=”section-faqs-about-microsoft-edit”>FAQs about Microsoft Edit
Here are some common questions regarding the Microsoft Edit tool on Windows 11.