Windows 11 offers a streamlined approach for users with multiple hard drives, allowing them to merge these drives into a single expansive volume. This not only simplifies data management but also minimizes the hassle of manually distributing data across various drives. Users can achieve this through two primary methods: the traditional Disk Management tool or the more contemporary Settings app.
How to span volume across drives using Disk Management
To create a large volume using Disk Management, follow these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Disk Management and select the top result to launch the application.
- Right-click on the drive volume and choose the Delete volume option if necessary.
- Confirm the deletion by clicking Yes.
- Repeat the previous two steps for any additional drives you wish to combine.
- Right-click on the unallocated space of one of the drives and select either “New Spanned Volume” or “New Striped Volume”.
- Click the Next button.
- Select the drives to include and click the Add button, noting that you can only add one drive at a time.
- Click Next.
- Choose a drive letter from the “Assign the following drive letter” setting.
- Click Next.
- Utilize the default file system and allocation unit size, then confirm a label for the drive.
- Check the “Perform a quick format” option and click Next.
Upon completing these steps, the system will successfully create a large volume that integrates the selected drives.
It’s important to note that the “New Spanned Volume” option writes files sequentially across each drive, which means that if one drive fails, the data on that drive is lost while the remaining data remains accessible. Conversely, the “New Striped Volume” option distributes data across multiple drives, enhancing read and write performance, but if one drive fails, the entire volume becomes inaccessible. Both options require a minimum of two drives and do not replace a RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) controller, which offers data redundancy and improved performance.
Extend volume already with data
If you have a drive with existing data, you can still extend its volume using additional hard drives by following these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Disk Management and select the top result.
- Right-click on the drive volume and select the Extend Volume option.
- Click Next.
- Select the drives to include in this process and click the Add button.
- Click Next.
- Click the Finish button.
- Confirm by clicking Yes to convert the drives to dynamic disks.
After completing these steps, the volume will extend to the selected drives without erasing existing data. However, it is prudent to back up your data before proceeding, even though this process is non-destructive.
How to span volume across drives using Settings
For those who prefer the Settings app, combining multiple drives into a single large volume can be accomplished as follows:
- Open Settings.
- Navigate to System.
- Click on the Storage page on the right side.
- Under the “Storage management” section, select “Advanced storage settings”.
- Click on Storage Spaces.
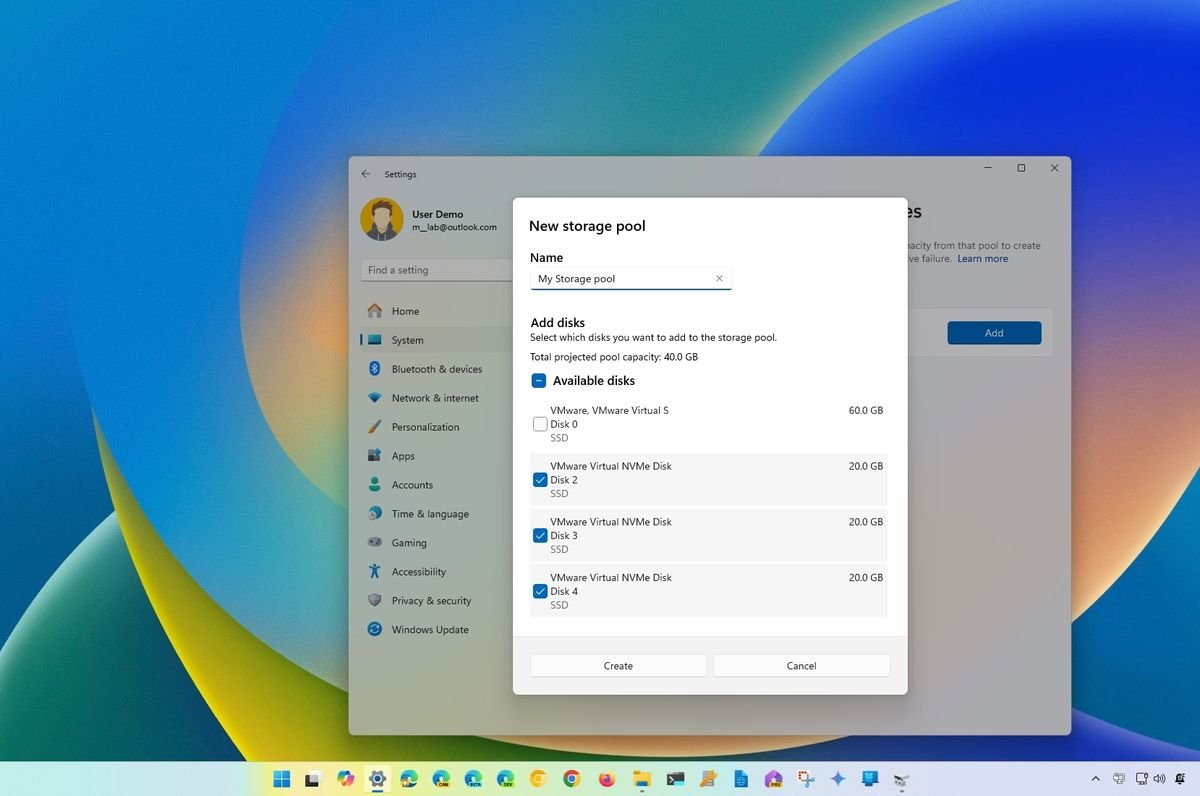
- Click the Add button under the “Pools” section.
- Provide a name for the pool, like “My Storage Pool,” and select the drives to combine.
- Click the Create button and confirm a name for the space.
- Use the default capacity in the “Size & resiliency” setting.
- Select the “Simple (no resiliency)” option or the Parity option.
- Click Create and confirm a label for the volume.
- Select a drive letter.
- Choose the NTFS option for the file system.
- Click the Format button.
Once these steps are completed, the Storage Spaces feature will generate a large volume that combines the drives with the selected resiliency. The “Simple” option creates a large volume without data protection, while the “Parity” option requires at least three drives and offers a safety net against hardware failure.
While both Storage Spaces and RAID technologies serve to combine multiple physical drives into a single logical unit, they differ in implementation and flexibility. Storage Spaces offers a software-only solution that allows for dynamic changes post-setup, whereas RAID can provide superior performance but is often more complex to manage. It’s essential to remember that these instructions apply only to secondary drives, as the boot drive requires a RAID solution for redundancy.
More resources
For further insights and guidance on Windows 10 and Windows 11, consider exploring additional resources that cover a wide range of topics and frequently asked questions.