Managing and monitoring the network’s IP address infrastructure becomes a streamlined process with the implementation of IP Address Management (IPAM) on Windows Server. This feature not only simplifies the tracking of IP address usage but also enhances the management of DHCP and DNS servers, ensuring adherence to network policies.
What is IPAM in Windows Server?
IPAM is a robust feature within Windows Server that automates and centralizes the management of IP address infrastructure. It empowers administrators to effectively monitor, manage, and audit DHCP and DNS servers while keeping a close eye on IP address allocation throughout the network.
How to setup IPAM on Windows Server?
Setting up IPAM on Windows Server involves a series of methodical steps:
- Verify Prerequisites
- Install IPAM
- Configure IPAM in the Windows Server
- Configure server discovery
- Manage servers and settings
1] Verify Prerequisites
Before diving into the IPAM setup, it’s crucial to address some essential prerequisites. Ensure that the server is running a supported version of Windows Server and is part of an active directory domain. Additionally, confirm that both DHCP and DNS roles are properly configured and operational. Once these checks are complete, you can proceed to the next step.
2] Install IPAM
With prerequisites verified, the next phase is to install IPAM on the Windows server. Here’s how:
- Open the Server Manager Console in Windows Server and navigate to the Local Server section.
- Click on the Manage tab, select Add Roles and Features, and proceed by clicking Next in the wizard.
- Choose Role-based or feature-based installation, hit Next, and then select Select a Server from the server pool.
- Pick the server for IPAM installation and click Next twice.
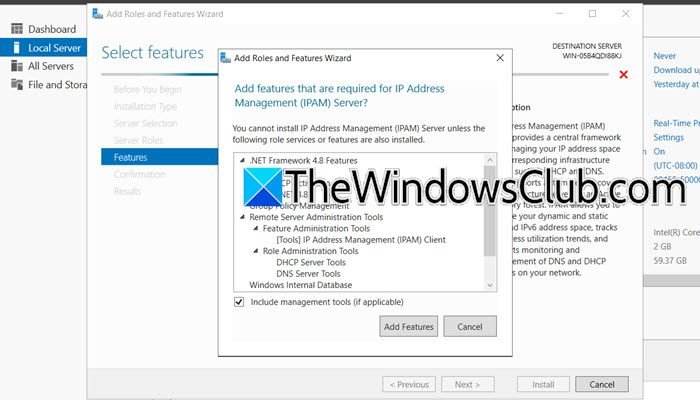
- On the Features page, locate and select IP Address Management (IPAM) server. A new window will appear; click Add Features, then select Next, and finally click Install.
Alternatively, IPAM can be installed via the command prompt using the following command:
Install-WindowsFeature IPAM -IncludeManagementToolsOnce the installation wizard completes, click Close to proceed to the configuration stage.
3] Configure IPAM in the Windows Server
Following installation, the next step is to configure IPAM to enable file sharing and access settings on the manager server. This configuration is vital for communication between the IPAM server and the manager server:
- Select IPAM from the left pane in Server Manager and click on Provision the IPAM server.
- Click Next, choose a database for storing IPAM server data (WID is recommended), and click Next again. If opting for an alternate database, ensure to check the Create a new Schema box.
- Select Group-based Policy, enter a GPO prefix in the GPO name prefix box, and click Next.
- Review all settings and click Apply to save changes.
A confirmation message will appear, indicating successful IPAM provisioning.
4] Configure server discovery and settings
The subsequent step involves configuring server discovery and settings:
- On the IPAM Overview page, click Configure server discovery. In the wizard, click Get Forests, wait a moment, and then click OK.
- Select the domains you wish the IPAM server to manage from the drop-down menu and click Apply.
- Return to the Overview page, click on Start Server discovery to initiate the discovery process for servers in the selected domain, and wait for completion.
5] Manage servers and settings
Once the server list is compiled, it’s time to add them to IPAM for management and verify their access status:
- Click on Select or Add servers to manage and verify the IPAM access link to include specific servers in the IPAM inventory. If access is blocked, indicating missing Group Policy Objects, open PowerShell as an administrator and execute the following command:
Invoke-IpamGpoProvisioning –Domain mylab.local –GpoPrefixName MYLAB_IPAM –IpamServerFqdn WS2K19-SRV02.mylab.local -DelegatedGpoUser [email protected]- Next, launch Group Policy Management and confirm that the IPAM GPO is listed under your domain.
- On your domain controller, open Command Prompt as an administrator and run
gpupdate /force. - Once completed, right-click on the server, select Edit Server, navigate to the Manageability status drop-down menu, and select Managed > OK. Then, right-click the server again and click on Retrieve server access status to refresh and verify the server’s access status.
- Ensure that the IPAM access status is now unblocked, confirming successful integration with IPAM.
- Finally, right-click the server and select Retrieve All Server Data to gather DHCP, DNS, and other network data from the managed servers for effective monitoring.
With these steps completed, users are now equipped to utilize the IPAM console to efficiently manage their network’s IP address infrastructure.
How do I add an IP address to IPAM?
To add an IP address to IPAM in Windows, access the IPAM console, navigate to the IP Address Space section, and select the desired IP Address block. Click on Add IP address and provide necessary details such as the IP address, status, associated device or client, and any relevant custom fields. Save the changes, and the new IP address will be successfully integrated into the IPAM database.