With the introduction of Windows 11 version 24H2 (2024 Update), users can now benefit from a remarkable new feature known as Windows Recall. This innovative tool, powered by artificial intelligence, acts as a digital photographic memory, capturing and remembering your on-screen activities. By taking regular screenshots and utilizing advanced on-device AI models, Windows Recall makes your past activities easily searchable through natural language queries via the dedicated “Recall” app.
How to configure and manage settings on Windows Recall
For those equipped with a Copilot+ PC, Windows Recall offers a variety of settings to tailor the experience to your needs. Users can opt in or out of the feature, adjust storage allocations, delete snapshots, and filter specific apps and websites.
Opt-in and out
Windows 11 does not enable the Recall AI feature by default; the choice lies with you. To toggle the feature on or off, follow these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Privacy & security.
- Select the Recall & snapshots page from the right side.
- (Option 1) Activate the “Save snapshots” toggle switch to enable the feature.
- (Option 2) Deactivate the “Save snapshots” toggle switch to disable it.
Upon completing these steps, the feature will either operate or remain inactive based on your configuration. Alternatively, you can enable the feature directly through the “Recall” app.
Change storage settings
By default, Windows Recall allocates 25GB of storage for devices with a 256GB SSD, 75GB for a 512GB SSD, and 150GB for a 1TB SSD. However, you have the flexibility to adjust this allocation:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Privacy & security.
- Select the Recall & snapshots page from the right side.
- Click the Storage setting.
- Choose your desired storage allocation size using the “Maximum storage for snapshots” setting.
- (Optional) Click the “View system storage” settings to check the drive usage of Recall AI.
- Select the data retention time range (Unlimited, 30, 60, 90, or 180 days) in the “Maximum storage duration for snapshots” setting.
After completing these steps, the system will apply your new storage allocation settings.
Delete snapshots
Windows Recall captures screenshots at regular intervals to analyze screen activity. However, to maintain privacy, users can delete specific snapshots or all stored data:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Privacy & security.
- Select the Recall & snapshots page from the right side.
- Click the Delete setting.
- (Option 1) Choose a timeframe to delete snapshots from the “Delete snapshots from a specific timeframe” setting, then click the Delete snapshots button.
- Click the Delete button again to confirm.
- (Option 2) Click the “Delete all” button to remove all snapshots stored on your computer.
- Click the Delete button again to confirm.
Once completed, the Recall data will be deleted as per your selections.
Filter sensitive information
To enhance privacy, Recall AI includes a feature that detects and filters out sensitive information, such as passwords and credit card details. This feature is generally enabled by default but can be managed from the “Recall & snapshots” settings:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Privacy & security.
- Select the Recall & snapshots page from the right side.
- (Option 1) Enable the “Filter sensitive information” toggle switch.
- (Option 2) Disable the “Filter sensitive information” toggle switch.
After these steps, the feature will either save or exclude sensitive information in snapshots.
Filter apps from Recall
Windows Recall records nearly all activities, but users can filter specific apps and websites from being monitored. By default, activities in Chromium-based browsers like Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome, as well as Mozilla Firefox and Opera in private modes, are not recorded. To exclude apps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Privacy & security.
- Select the Recall & snapshots page from the right side.
- Click the Add app button to filter an app.
- Select the app from the list and click the Add button.
To remove an app, follow the same steps but click on the “Apps to filter” setting and then click the “Remove” button for the desired app.
Filter websites from Recall
To exclude specific websites from being recorded, follow these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Privacy & security.
- Select the Recall & snapshots page from the right side.
- Click the Add website button.
- Confirm the website to exclude and click the Add button.
Similar to filtering apps, you can remove websites using the same instructions, but in step 4, click on the “Websites to filter” setting and then click the “Remove” button for the website you wish to exclude.
Pause and resume
Users can also pause and resume Recall snapshots with ease:
- Click the Windows Recall button from the System Tray.
- (Option 1) Click the “Pause until tomorrow” button to disable the feature until the next day at 12 AM.
- (Option 2) Click the “Resume snapshots” button to manually turn the feature back on.
The Recall flyout menu also displays the last snapshot taken and its status, along with options to access more settings.
How to search and find activities on Windows Recall
Once configured, Windows Recall provides a straightforward way to search for past activities:
- Click the Windows Recall button in the System Tray.
- Sign in with your Microsoft account credentials.
- Click the Open Recall button.
- (Option 1) Use the search box to query an activity using natural language.
- Select the snapshot from the results.
- (Option 2) Use the timeline slider to scroll back in time to find a specific snapshot.
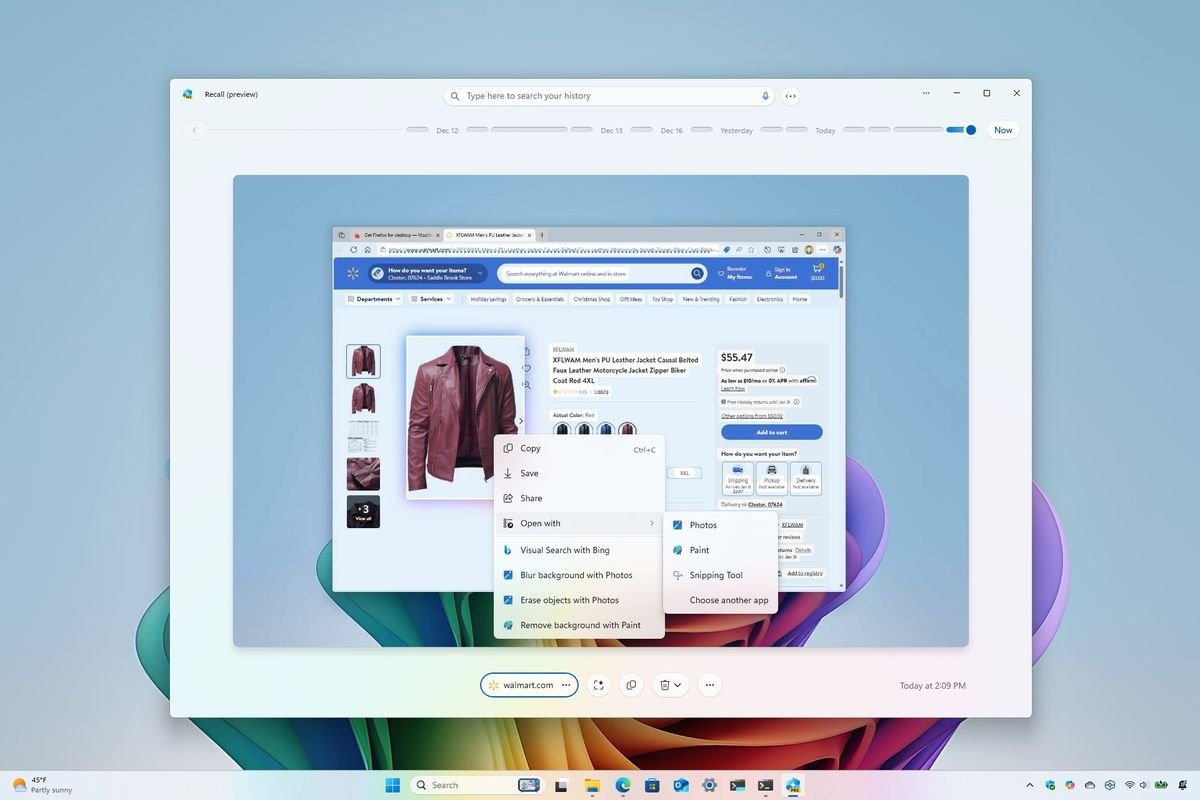
For example, you might type, “find the red leather jacket I saw the other day when browsing the internet.” The feature will sift through your past activities to retrieve relevant snapshots.
Interact with snapshots
When interacting with snapshots, users can utilize the “Click to Do” feature, which analyzes the contents of the snapshots to present actionable options:
- Open the Windows Recall app.
- Sign in using Windows Hello.
- Perform a search or use the timeline slider.
- Select the snapshot from the results.
- Interact with elements within the snapshot, which will be highlighted for easy identification.
This feature allows users to copy text, blur backgrounds, or erase objects directly from the snapshot, enhancing the overall utility of the Recall tool.
Other details about Windows Recall
Windows Recall operates only while the device is actively in use. If the computer becomes idle, the feature will automatically disable until activity resumes. The System Tray icon serves as an indicator of the feature’s status, remaining visible unless the feature is turned off.
Disabling Windows Recall will not delete existing data; however, it will prevent future snapshots from being taken. Users can manually delete snapshots if they wish to clear their history. Microsoft has implemented additional security measures, including encryption of the Recall database and snapshots, ensuring that data remains secure and private.
Importantly, the data collected by Recall remains on the user’s device, with no uploads to the cloud or usage for AI training purposes. The feature is currently optimized for several languages, including English, Chinese (simplified), French, German, Japanese, and Spanish.
More resources
For additional articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10 and Windows 11, consider exploring the following resources: